A study on detection capability of the Inner Mongolia regional seismic network
-
摘要: 国际上新近发展的“基于概率的完整性震级”(PMC)方法,具有可考察地震定位中由于台站人为选择等造成的台网监测能力下降,以及避免传统基于G-R关系的统计算法因地震数目过少而无法评估等优点.本研究利用PMC方法,计算得到内蒙古区域地震台网39个台站对周边地震事件的检测概率及台网检测概率.单台检测概率结果显示:PMC方法能够客观地反映39个台站对地震事件的检测能力;因台网布局等影响,内蒙古区域地震台网中西部和中东部地区的台站检测能力较强,而靠近蒙古、俄罗斯边境的台站, 阿拉善右旗附近地区的台站,以及邻近吉林、黑龙江等地区的台站检测能力较低.合成检测概率结果显示,由于邻省台站的引入,全区80%的地区基于概率的最小完整性震级MP达到2.2左右,其余地区MP达到3.3左右.为提高地震台网监测能力,建议在监测能力较弱的中蒙交界地区、东北部地区,以及阿拉善左旗以西地区适度加密台站,进一步优化台网布局.
-
关键词:
- 内蒙古区域地震台网 /
- 最小完整性震级 /
- 基于概率的完整性震级方法
Abstract: As a new developed method for estimating earthquake detection probabilities, the probability-based magnitude of completeness (PMC) method can avoid decreasing the detection capability resulted by artificial factors, and can access the detection capability in the areas where traditional Gutenberg-Richter relationship-based method is ineffective due to lack of earthquakes. In this study, we determine the detection probability of all 39 stations of the Inner Mongolia seismic network by using the PMC method. The results show that the PMC method can reflect the network earthquake monitoring capacity objectively. The detection probability is better than other regions in the midwestern and the mid-eastern region of Inner Mongolia, due to better coverage of seismic stations, however, it is poor in the Alxa Youqi region, the Sino-Russian border, and Sino-Mongolia border. Synthesized detection probability results indicate that minimum probability-based magnitude of completeness, MP, can reach ML2.2 in the 80% area of the Inner Mongolia when the stations of the neighboring networks are involved, and only about ML3.3 in other areas. In order to enhance the monitoring capacity of Inner Mongolia regional seismic network, more stations are still needed to emplace in the Sino-Mongolia border region, the northeastern region of Inner Mongolia, and to the west of Alxa Zuoqi to optimize the layout of seismic network. -
引言
对地震台网监测能力的科学评估,是开展地震危险性分析、区域速度结构探查等地球科学研究的重要基础(Stein,1999; Knopoff,2000; Main,2000; Gomberg et al,2001; Enescu,Ito,2002; Wiemer,Wyss,2002; Woessner et al,2004).地震台网监测能力,一方面是指定位能力,目前常用的评估方法主要有考虑台站几何分布和台址条件等进行的监测能力理论评估(吴开统等,1991)、“参考事件”标定(郭飙等,2002)、不同台网定位结果对比(Wüster et al,2000)、使用统计算法评价其“优化”程度(Rabinowitz,Steinberg,1990; Doufexopoulou,Korakitis,1992; Bartal et al,2000)以及利用重复地震的分布和间距小于1 km的假定(Schaff,Richards,2004)描述监测能力空间分布(蒋长胜,吴忠良,2005; 蒋长胜等,2008)等.
而作为地震台网监测能力评估的另一个重要方面,即最小完整性震级 Mc,则多基于统计地震学方法进行评估.一般可分为两类:一类是假定震级不小于 Mc的地震在震级-频度分布上满足G-R关系(Gutenberg,Richter,1944)

并认为这些地震的记录是完整的(Wiemer,Wyss,2000; Cao,Gao,2002; Marsan,2003; Woessner,Wiemer,2005; Amorèse,2007);另一类则是基于非G-R关系的方法,例如基于概率的完整性震级(probability-based magnitude of completeness,简写为PMC)方法(Schorlemmer,Woessner,2008)和贝叶斯完整性震级(Bayesian magnitude of completeness,简写为BMC)方法(Mignan et al,2011,2013)等.
近年来,PMC方法得到了广泛关注,目前已在美国南加州地震台网(Schorlemmer,Woessner,2008)、瑞士(Nanjo et al,2010)和意大利(Schorlemmer et al,2010; Gentili et al,2011)等地区得到应用.PMC方法的主要优点在于:① 对最小完整性震级 Mc的分析依赖于地震台网的属性,不需要假定震级的分布关系;② 使用地震台网实际产出的地震观测报告的评估结果中涵盖了因未使用全部记录清晰台站定位等人为因素造成的台网监测能力的实际下降;③ 不存在因地震数目过少而无法估算的“空区”,这使得对区域台网整体空间的完整性评估成为可能;④ 评价精度较高,误差低于0.1个震级单位(Nanjo et al,2010).
内蒙古自治区横跨我国西北、华北和东北地区,地质构造复杂,地震活动较为强烈.内蒙古区域地震台网经过“九五”、“十五”和“十一五”的长期建设,地震监测能力显著提高,地震观测事业稳步发展.但由于地震台网建设受到地域狭长、行政区域划分不规则等限制,地震监测能力存在明显的区域不均衡,为该地区的地球科学研究带来了一定难度.本研究将在系统分析内蒙古区域地震台网观测资料和台网分布特征的基础上,利用PMC方法给出的台站检测概率来评估内蒙古区域地震台网的监测能力,并进一步提出优化台网布局的建议.
1. PMC方法的计算原理
基于概率的完整性震级(PMC)方法是基于区域地震震级定义和实际产出的震相观测报告,计算每个台站对全部地震在时空上的检测能力(Schorlemmer,Woessner,2008).利用“单台检测概率”PD得到“合成检测概率” PE,并计算出基于概率的完整性震级MP.
作为PMC方法的重要组成部分,每个台站的检测概率的计算步骤为:① 要求在研究时段内各台站地震震级的定义及台网对地震的触发条件保持不变;② 给出每个台站记录到的地震震级M与震中距L的对应情况,并将其作为计算台站检测概率的原始数据;③ 基于区域台网震级的定义,获得震级M与震中距L的经验换算关系.其相关计算原理如下:
对于区域地震台网,震级测定随距离的衰减关系一般可表示为

式中:A为仪器记录的振幅;L*为震中距;c1,c2和c 3为常数.在某个台站记录到的两次地震振幅均为A的情况下,测得的与两个事件震中距L1和L2相对应的震级分别为

在震级-距离二维图上表示的台站检测概率需要构建M与L的经验转换关系.将式(3)减去式(4)可得

上式中震级差ΔM*仅与震中距L有关.目前我国各个区域地震台网的地方震震级 ML的测定均采用同一种方法,即利用仿真短周期位移记录(DD-1或伍德-安德森仪器记录)的S波或Lg波最大振幅来测定(中国地震局监测预报司,2003),具体表达式为

式中R(L)为台站的量规函数.由此,式(5)中的ΔM*实际上仅与相应震中距L的量规函数R(L)有关.在计算震级-距离二维图上点位(M,L)所对应的台站检测概率时,需选定计算所用数据.Schorlemmer和Woessner(2008)定义了如下选取原则:
对台站周围发生的某次震级为M′、震中距为L′的地震事件,计算与点位(M,L)对应的震级差ΔM=M ′- M,以及利用式(5)和式(6)计算因不同距离引起的震级差ΔM*=R(L′)- R(L).数据遴选的度量条件采用如下形式(Schorlemmer,Woessner,2008;Gentili et al,2011):

当符合上述条件的地震事件数Nt≥10时,统计被台站检测到的地震事件数N+和未被检测到的地震事件数 N-,并计算台站在(M,L)处的检测概率为

“合成检测概率”PE(M,x,t)定义为在位置x、时刻t和震级M的地震能被台网中4个以上台站记录到的概率.综合各台结果,形成时刻t、震级M、位置x时的“合成检测概率”PE(M,x,t)和完整性震级MP(x,t).其相关计算原理如下:

式中,P0E,P1E,P2E和P3E分别表示一定位置和震级的地震能够被台网中0,1,2和3个台站记录到的概率.台站没有检测能力的概率为

使用组合式的方法,得到能够被j个台站记录到的概率为

依据式(9)—(11),得到“合成检测概率” PE(M,x,t)为

以此合成得到基于概率的完整性震级,各震级档下完整性震级为

其中取Q=0.0001(误差标准).
2. 资料
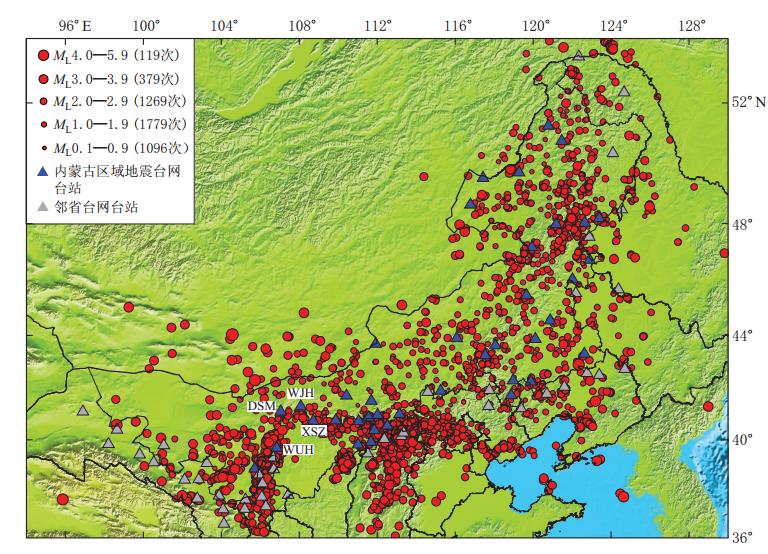
截至国家“十五”重大项目 “中国数字地震观测网络工程”2008年验收运行①,内蒙古区域地震台网共建成数字化地震台站39个,同时引入甘肃、宁夏、山西、河北、吉林、辽宁、黑龙江等邻省区域地震台网的43个地震台站组成地震监测网络,有效改善了以往地震台网布局不合理的状况,显著提高了内蒙古地区的地震监测能力.图1给出了2008年以来内蒙古区域地震台网的台站分布和ML0.0以上地震的空间分布.为考察内蒙古区域地震台网39个台站对地震事件的监测能力(以区别台网整体的“监测能力”),选取台网稳定运行的2008年10月—2013年8月的地震观测报告数据,利用PMC方法进行内蒙古区域地震台网监测能力的评估.
①:http://www.cea.gov.cn/manage/html/static/zgszdzgcwlxm/index.html. 查询日期:2013年10月1日.
3. 计算结果
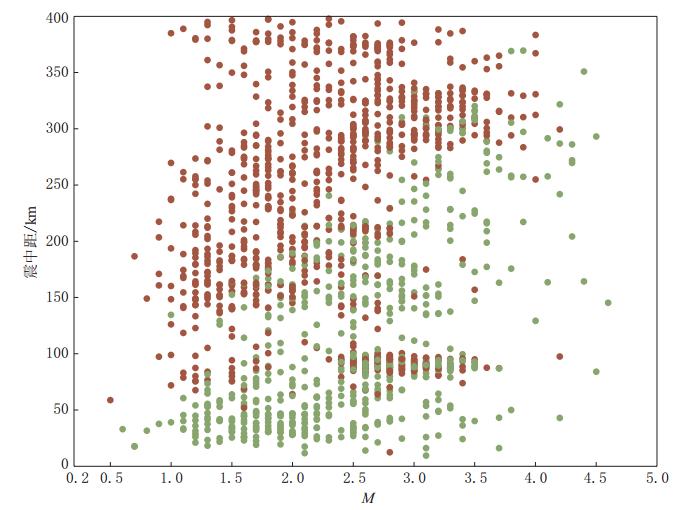
选取可被至少4个台站记录到的地震事件,利用PMC方法进行台站检测概率 PD的计算.由图2给出的乌海台(WUH)对周边地震的检测(即参与了该地震的定位)情况可见,随着震中距的增大,绿色圆点所示的被检测到地震的震级逐渐增大,监测能力逐渐下降;但同时,在被检测到的地震事件的分布范围内,也存在部分未被检测到的事件,表明乌海台并未用于全部可检测到地震事件的定位,这种对地震定位台站的人为选取可能会影响台站的检测能力.
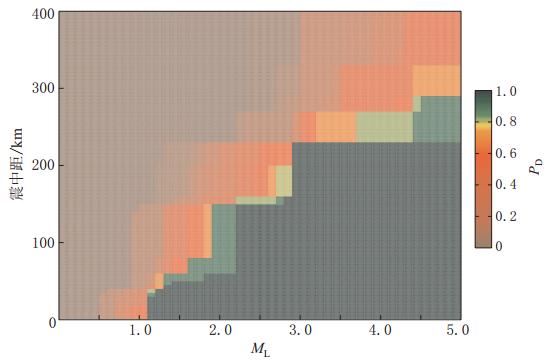
图3给出了乌海台的 PD(M,L)计算结果.由该图可见,当 ML=1.0时,PD未达到100%;当ML=4.0时,PD=100%所对应的震中距L值 范围为0—220 km;在L=100 km处,PD达到100%对应的震级约为 ML2.3;在 L =300 km处,PD未达到100%.
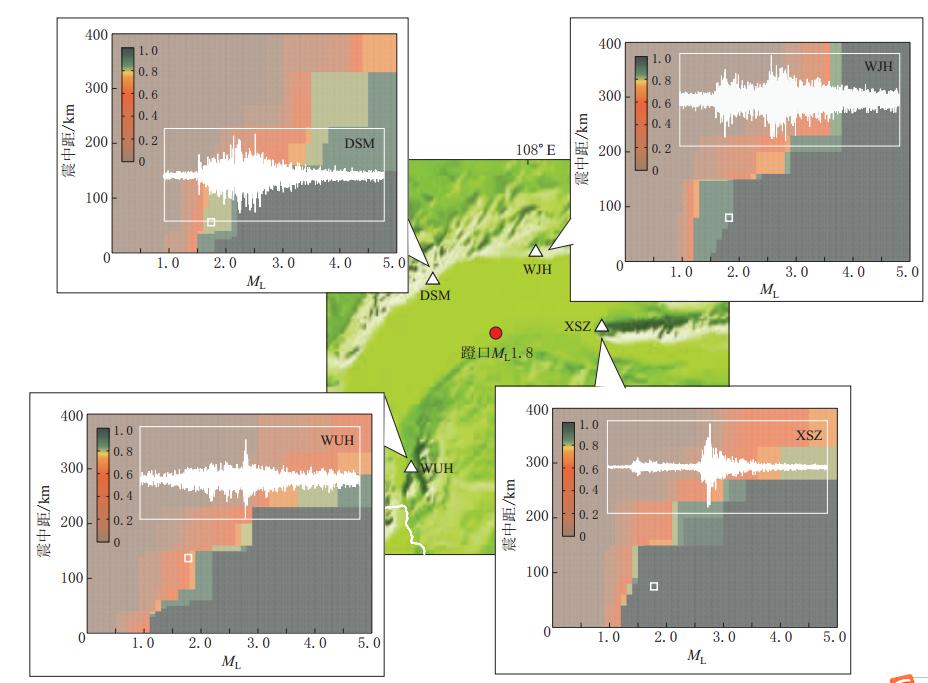
为考察 PD能否接近真实地反映台站对地震事件的检测能力,本文以2009年1月6日内蒙古磴口 ML1.8地震(震中40°42′N,107°41′E,深度8.8 km)为例,分析PD及实际地震波形记录信噪比情况.如图4所示,参与此次地震定位的4个台站分别为东升庙(DSM)、乌加河(WJH)、乌海(WUH)和西山嘴(XSZ).其中:西山嘴和乌加河两台记录信号清晰,对应的震中距和震级的PD值高;东升庙台记录信号较清晰,PD值也相对较高;乌海台记录信号较弱,PD值较低.对比各台站的检测概率和对直达P波震相的波形记录可见,台站的 PD值高低可以真实地反映地震记录信号的强度.
![]() 图 4 2009年1月6日内蒙古磴口 ML1.8地震和4个记录台站的检测概率图中各子图分别给出了DSM,WJH,WUH和XSZ台的检测概率以及波形记录情况,其中波形进行了0.5 Hz的高通滤波,图中白色方块标出了地震在相应的震中距和震级所对应的检测概率Figure 4. Detection probabilities and seismograms of the Dengkou,Inner Mongolia,ML1.8 earthquake on 6 January 2009 The insets contain detection probability distributions of four selected stations(DSM,WJH,WUH and XSZ). Small white squares mark the detection probability of each station for this particular event,given by its magnitude and respective distance to the stations. Seismograms filtered through 0.5 Hz high-pass filter are shown as overlays in white frames
图 4 2009年1月6日内蒙古磴口 ML1.8地震和4个记录台站的检测概率图中各子图分别给出了DSM,WJH,WUH和XSZ台的检测概率以及波形记录情况,其中波形进行了0.5 Hz的高通滤波,图中白色方块标出了地震在相应的震中距和震级所对应的检测概率Figure 4. Detection probabilities and seismograms of the Dengkou,Inner Mongolia,ML1.8 earthquake on 6 January 2009 The insets contain detection probability distributions of four selected stations(DSM,WJH,WUH and XSZ). Small white squares mark the detection probability of each station for this particular event,given by its magnitude and respective distance to the stations. Seismograms filtered through 0.5 Hz high-pass filter are shown as overlays in white frames4. 内蒙古区域地震台网各台站检测概率的对比分析
为定性地评估内蒙古区域地震台网39个台站对地震事件检测能力的差异,本文尝试利用以下条件来评估:① M=ML1.0时 PD是否达到100%;② M=ML4.0时 PD=100%所对应震中距L的数值范围;③ 在 L =100 km处,PD=100%所对应的震级;④ 在 L=300 km处,PD是否达到100%.根据上述条件,将内蒙古区域地震台网39个台站 PD计算结果的评定结果列于表1.
表 1 内蒙古区域地震台网台站检测概率PD统计表Table 1. Detection probability,PD,of the stations of the Inner Mongolia regional seismic network
由表1可见,当M=ML1.0时,5个台站(QSH,HLG,LCH,CHR,ZLT)的PD可达100%,其余34个台站PD均低于100%;当M=ML4.0时,PD=100%对应的震中距范围为80—400 km;在L=100 km处,PD=100%对应的震级范围为1.9≤ML≤4.1,均值为ML1.95,只有3个台站(BHS,DOSH,CSQ)的PD未达到100%;在L=300 km处,7个台站(HHH,WJH,XIH,XLT,BYT,GNH,MDG)的PD=100%对应的震级范围为3.4≤ML≤4.4,其余32个台站检测概率均未达到100%,其中DOSH台检测概率最低.
根据表1的定性评估结果,进一步给出了内蒙古区域地震台网台站PD的区域特征结果,如表2所示.由表2可见,内蒙古中西部地区(38°—42°N,105°—114°E)的17个台站中,10个台站(WUH,DSM,XSZ,WJH,BTO,BLM,HHH,QSH,HLG,JIN)对较小震级事件有较高的检测能力,6个台站(WLH,BYT,RLT,LCH,CSQ,BHS)检测概率较低,1个台站(DOSH)几乎无检测能力;中东部地区(41.5°—46°N,115°—126°E)的12个台站中,8个台站(BAC,XLT,LIX,CHF,NIC,XIH,AGL,WLT)对较小地震有较高的检测能力,其余4个台站(LUB,HLH,JIP,TIS)的检测能力较低;东部地区(46°—53.5°N,115.5°—126°E)的10个台站中,5个台站(NJT,IDR,ARS,ZLT,CHR)对于震级较小的地震事件有较强的检测能力,其余5个台站(MZL,MDG,GNH,XIQ,HLR)的检测能力较低.
表 2 内蒙古区域地震台网不同区域的台站检测概率统计表Table 2. Statistical results of the regional detection probability of the stations of the Inner Mongolia regional seismic network
5. 内蒙古区域地震台网监测能力评估
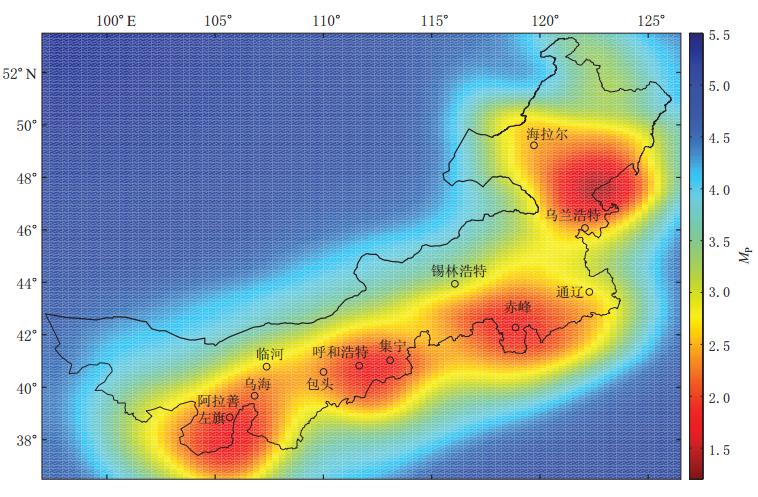
基于概率的完整性震级 MP反映了台网监测能力在空间上的分布特征.依据82个单台的检测概率,得到了内蒙古区域地震台网的 MP分布(图5).可以看到:由于邻省台站的引入,使得内蒙古乌兰浩特—扎兰屯一带及蒙黑交界地区最小完整性震级达到最低(MP≤1.5),监测能力最强;正蓝旗—赤峰—通辽一带及辽蒙交界、呼和浩特—包头—集宁一带及晋蒙交界、临河—乌海—巴彦浩特一带及蒙甘宁交界,1.5≤ MP≤2,0,以及MP为2. 5左右的海拉尔地区,监测能力较强;与蒙古交界的地区(100°—118°E)MP为3.5左右,监测能力较弱;阿拉善左旗以西—阿拉善右旗(103°E以西)MP为5.0左右,监测能力最弱.全区80%的地区MP达到2.2左右,其余地区MP达到3.3左右.
综合上述结果,建议在内蒙古与蒙古交界地区、东北部地区、阿拉善左旗以西地区增设台站,以提高内蒙古区域地震台网的整体监测能力.
6. 讨论与结论
内蒙古区域地震台网影响台站检测概率的原因可能包括:① 台站分布稀疏且相对分布不均,本文为确保结果的可靠性而筛选4个以上P波到时记录到的事件进行计算,导致M=ML1.0时多数台站PD未达到100%;② 部分靠近边境地区或邻省引入共享台站数量偏少地区的台站,受台站分布方位的影响PD较低;③ DSH台(井下摆)因2008年8月雨季进水后被撤掉,而后于2009年1月在原址上重建,运行了东胜台(地面摆),但受雷击等原因该台运行一直不稳定,运行期间仅对55次地震事件在定位中使用,致使东胜台的PD值最低;④ 由于在地震定位实际操作中以“降低定位残差、提高定位精度”为优先原则,以及人为舍弃震中距较大或震相相对不清楚的台站等因素的影响,可能导致部分台站的检测概率降低.
由于PMC方法要求台站周边的地震活动具有均匀性,所以实际地震活动在时空上的丛集分布可能会在一定程度上影响PD的计算结果.此外,PMC方法假定台站对不同方位地震的监测能力具有各向同性,这与实际情况也可能存在差异,例如在矿山等 小尺度区域(Plenkers et al,2011).
为科学地评估内蒙古区域地震台网的地震监测能力,本研究采用目前国际上新近发展的PMC方法,计算获得了内蒙古区域地震台网39个台站的检测概率,并得到如下认识:
1)利用PMC方法获得的内蒙古区域地震台网“十五”时期台站的检测概率,可以反映台站地震事件的实际检测情况.
2)由于受台网分布稀疏、空间分布不均匀等因素影响,不同区域的台站检测能力存在差异,其中内蒙古中东部与中西部地区台站的检测能力比较接近,而东部地区台站检测能力总体偏低;靠近蒙古、俄罗斯边境的台站,以及邻近无台站的阿拉善右旗地区和邻近吉林省、黑龙江省的台站检测能力普遍偏低,是需要优化台网布局的区域.
3)在地震定位中对台站的人为不合理遴选,可能会导致台站检测能力的实质性降低.
通过对内蒙古区域地震台网监测能力的评估,认为全区80%的地区MP达到了2.2左右,其余地区 MP达到3.3左右.建议在内蒙古与蒙古交界地区、东北部地区及阿拉善左旗以西地区增设台站,以提高内蒙古地区的整体监测能力.
德国亥姆霍兹地球科学中心(GFZ)的Danijel Schorlemmer教授为本研究提供了计算程序,“地震可预测性合作研究”(CSEP)项目中国检验中心筹备组专家对本文工作给予了指导,在此一并表示感谢.
-
图 4 2009年1月6日内蒙古磴口 ML1.8地震和4个记录台站的检测概率图中各子图分别给出了DSM,WJH,WUH和XSZ台的检测概率以及波形记录情况,其中波形进行了0.5 Hz的高通滤波,图中白色方块标出了地震在相应的震中距和震级所对应的检测概率
Figure 4. Detection probabilities and seismograms of the Dengkou,Inner Mongolia,ML1.8 earthquake on 6 January 2009 The insets contain detection probability distributions of four selected stations(DSM,WJH,WUH and XSZ). Small white squares mark the detection probability of each station for this particular event,given by its magnitude and respective distance to the stations. Seismograms filtered through 0.5 Hz high-pass filter are shown as overlays in white frames
表 1 内蒙古区域地震台网台站检测概率PD统计表
Table 1 Detection probability,PD,of the stations of the Inner Mongolia regional seismic network

表 2 内蒙古区域地震台网不同区域的台站检测概率统计表
Table 2 Statistical results of the regional detection probability of the stations of the Inner Mongolia regional seismic network

-
郭飙, 刘启元, 陈九辉, 李顺成. 2002. 首都圈数字地震台网的微震定位实验[J]. 地震地质, 24(3): 453-460. Guo B, Liu Q Y, Chen J H, Li S C. 2002. Test of epicenter determination of micro earthquakes recorded by the digital seismic network in capital circle[J]. Seismology and Geology, 24(3): 453-460 (in Chinese).
蒋长胜, 吴忠良. 2005. 由"重复地震"给出的中国地震台网的定位精度估计[J]. 中国地震, 21(2): 147-154. Jiang C S, Wu Z L. 2005. Estimating the location accuracy of the China National Seismograph Network using repeating events[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 21(2): 147-154 (in Chinese).
蒋长胜, 吴忠良, 李宇彤. 2008. 首都圈地区"重复地震事件"及其在区域地震台网定位精度评价中的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(3): 817-827. Jiang C S, Wu Z L, Li Y T. 2008. Estimating the location accuracy of the Beijing Capital Digital Seismograph Network using repeating events[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(3): 817-827 (in Chinese).
吴开统, 焦远碧, 杨满栋. 1991. 中国地震台网布局的优化方案[J]. 地震学刊, (1): 22-37. Wu K T, Jiao Y B, Yang M D. 1991. An optimum scheme for distribution of seismic station networks in China[J]. Journal of Seismology, (1): 22-37 (in Chinese).
中国地震局监测预报司. 2003. 数字地震观测技术[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 521-522. Department of Monitoring and Prediction, China Earthquake Administration. 2003. Digital Seismic Observation Technique[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 521-522 (in Chinese).
Amorèse D. 2007. Applying a change-point detection method on frequency-magnitude distributions[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 97(5): 1742-1749.
Bartal Y, Somer Z, Leonard G, Steinberg D M, Horin Y B. 2000. Optimal seismic networks in Israel in the context of the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 90(1): 151-165.
Cao A M, Gao S S. 2002. Temporal variation of seismic b-values beneath northeastern Japan island arc[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 29(9): 1334. doi:10.1029/2001GL013775.
Doufexopoulou M, Korakitis R. 1992. Resolution analysis of seismic networks[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 75(1/2/3): 121-129.
Enescu B, Ito K. 2002. Spatial analysis of the frequency-magnitude distribution and decay rate of aftershock activity of the 2000 Western Tottori earthquake[J]. Earth Planets Space, 54(8): 847-859.
Gentili S, Sugan M, Peruzza L, Schorlemmer D. 2011. Probabilistic completeness assessment of the past 30 years of seismic monitoring in northeastern Italy[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 186(1/2): 81-96.
Gomberg J, Reasenberg P, Bodin P, Harris R. 2001. Earthquake triggering by seismic waves following the Landers and Hector Mine earthquakes[J]. Nature, 411(6836): 462-466.
Gutenberg R, Richter C F. 1944. Frequency of earthquakes in California[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 34(4): 185-188.
Knopoff L. 2000. The magnitude distribution of declustered earthquakes in Southern California[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 97(22): 11880-11884.
Main I. 2000. Apparent breaks in scaling in the earthquake cumulative frequency-magnitude distribution: Fact or artifact?[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 90(1): 86-97.
Marsan D. 2003. Triggering of seismicity at short timescales following Californian earthquakes[J]. J Geophys Res, 108(B5): 2266. doi:10.1029/2002JB001946.
Mignan A, Werner M J, Wiemer S, Chen C C, Wu Y M. 2011. Bayesian estimation of the spatially varying completeness magnitude of earthquake catalogs[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 101(3): 1371-1385.
Mignan A, Jiang C S, Zechar J D, Wiemer S, Wu Z, Huang Z B. 2013. Completeness of the mainland China earthquake catalog and implications for the setup of the China Earthquake Forecast Testing Center[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 103(2A): 845-859.
Nanjo K Z, Schorlemmer D, Woessner J, Wiemer S, Giardini D. 2010. Earthquake detection capability of the Swiss Seismic Network[J]. Geophys J Int, 181(3): 1713-1724.
Plenkers K, Schorlemmer D, Kwiatek G, JAUARS Research Group. 2011. On the probability of detecting picoseismicity[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 101(6): 2579-2591.
Rabinowitz N, Steinberg D K. 1990. Optimal configuration of a seismographic network: A statistical approach[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 80(1): 187-196.
Schaff D P, Richards P G. 2004. Repeating seismic events in China[J]. Science, 303(5661): 1176-1178.
Schorlemmer D, Woessner J. 2008. Probability of detecting an earthquake[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 98(5): 2103-2117.
Schorlemmer D, Mele F, Marzocchi W. 2010. A completeness analysis of the national seismic network of Italy[J]. J Geophys Res, 115(B4): B04308. doi:10.1029/2008JB006097.
Stein R S. 1999. The role of stress transfer in earthquake occurrence[J]. Nature, 402(6762): 605-609.
Wiemer S, Wyss M. 2000. Minimum magnitude of complete reporting in earthquake catalogs: Examples from Alaska, the Western United States, and Japan[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 90(4): 859-869.
Wiemer S, Wyss M. 2002. Mapping spatial variability of the frequency-magnitude distribution of earthquakes[J]. Adv Geophys, 45(Ⅰ/Ⅱ/Ⅲ/Ⅳ/Ⅴ): 259-302.
Woessner J, Hauksson E, Wiemer S, Neukomm S. 2004. The 1997 Kagoshima (Japan) earthquake doublet: A quantitative analysis of aftershock rate changes[J]. Geophys Res Lett, 31(3): L03605. doi:10.1029/2003/GL018858.
Woessner J, Wiemer S. 2005. Assessing the quality of earthquake catalogs: Estimating the magnitude of completeness and its uncertainties[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 95(4): 684-698.
Wüster J, Rivière F, Crusem R, Plantet J, Massinon B, Caristan Y. 2000. GSETT-3: Evaluation of the detection and location capabilities of an experimental global seismic monitoring system[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am, 90(1): 166-186.
-
期刊类型引用(35)
1. 杨周胜,杨晶琼,刘鹏飞,吕帅,姚远. 基于概率的震级完备度方法评估云南地震台网的监测能力. 地震研究. 2025(01): 61-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张帆,韩晓明,包金哲,杨晓忠. 基于贝叶斯方法的首都圈地区完整性震级评估. 地震学报. 2025(01): 107-121 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 梁向军,吴叔坤,王霞,刘林飞. 用不同方法评估山西地震台网的监测能力. 山西地震. 2024(01): 38-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 翟浩,王勇,王禄军. 内蒙古测震台网实时智能地震处理系统运行实践——以2020年和林格尔地区地震事件为例. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2024(02): 158-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 高智刚. 鄂尔多斯块体周缘最小完备性震级测定及b值时空分布特征研究. 科技创新与应用. 2024(22): 86-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张帆,杨晓忠,崔丰智. 鄂尔多斯地块北缘地震检测概率和地震目录完整性分析(英文). Applied Geophysics. 2024(04): 777-793+881 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 潘国勇,夏波,刘菲,王成睿,王军,林航毅,周伯昌. 上海测震台网数据质量综合分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2023(02): 64-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 立凯,何奕成,宫杰,何浩宇,秦磊,霍祝青. PMC方法在江苏测震台网监测能力评估中的应用. 震灾防御技术. 2023(03): 642-650 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 赵艳红,翟浩,胡炜,舒雷. 内蒙古地震重大项目监测台网监测能力评估. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2023(04): 34-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 王鹏 ,魏薇 ,蔡旭荣 ,刘菲 ,王成睿 . 长三角区域地震监测能力分析. 科技与创新. 2022(08): 76-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 梁向军,宋美琴,刘芳,刘林飞. 利用PMC方法评估山西测震台网的地震监测能力. 华北地震科学. 2022(02): 62-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 郭瑛霞,张丽峰,黄浩,李振凯,胡维云. 祁连带中东段b值时空特征研究. 高原地震. 2022(03): 16-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 彭利媚,刘林飞,陈祥开,曾维顺,丁有兴,孙佩雯,李健,李冬雅. 利用PMC方法评估海南测震台网地震监测能力. 华南地震. 2022(03): 21-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 郭瑛霞,张丽峰,顾勤平,黄浩,李振凯,马丽. 基于PMC方法评估青海省测震台网监测能力. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2022(05): 23-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 余洋洋,戴仕贵,杜瑶,王宇玺,庄园旭. 四川泸州地区测震台网地震监测能力研究. 中国地震. 2021(01): 227-238 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 张晖,谭毅培,马婷,翟浩,张珂,李娟. 2020年和林格尔M_L4.5地震微震匹配定位及发震构造探讨. 中国地震. 2021(02): 430-441 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 李娟,韩晓明,张帆. 2015-04-15阿拉善左旗5.8级地震前后构造应力场研究. 大地测量与地球动力学. 2020(09): 923-927 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 王鹏,毕波,林航毅,刘菲,邵永谦,王军. 基于PMC方法的上海测震台网地震监测能力评估. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2020(05): 18-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 李瑞红. 基于地脉动噪声的呼伦贝尔地区监测能力研究. 防灾减灾学报. 2019(01): 58-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 安祥宇,赵倩,王晓睿,王淑辉,徐鹏深. 基于PMC方法的辽宁测震台网监测能力评估. 地震工程学报. 2019(06): 1545-1552 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 赵艳红,张帆,娜热. 内蒙古东部地区一维地壳速度结构分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2018(01): 41-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 赵艳红,张帆,苏亚梅. 内蒙古测震台网台站布局对地震定位的影响. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2018(04): 88-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 马援,刘甜甜,贾浩东. 宝昌地震台VP型垂直摆倾斜仪常见干扰. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2018(04): 183-188 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 刘栋,韦永祥. 基于概率完备震级评估福建省测震台网监测能力. 科学技术创新. 2018(10): 28-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. Zhao Yanhong,Jia Xiye. The Crustal Velocity Structure of Western Inner Mongolia. Earthquake Research in China. 2018(01): 89-99 .  必应学术
必应学术
26. Liu Yongmei,Liu Fang,Liu Gaimei,Zhang Fan. The Focal Depth Analysis of the Inner Mongolia-Ningxia Border Area Earthquakes. Earthquake Research in China. 2018(02): 233-244 .  必应学术
必应学术
27. 张帆,刘永梅,郝美仙,韩晓明,李娟,赵星,候迪. 内蒙古阿拉善地区几次中等强度地震震源深度测定. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2017(02): 38-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
28. 魏建民,韩晓明,张帆,李彬. 2015年4月15日阿拉善左旗M_S 5.8地震序列特征. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2017(01): 32-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
29. 李娟,韩晓明,王晓山,杨红樱,张帆,张晖. 呼和浩特—包头盆地震源应力场状态分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2017(02): 57-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
30. 杨红樱,刘永梅,赵星,王勇. 包头地震台形变干扰分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2017(03): 153-158 .  百度学术
百度学术
31. 刘永梅,刘芳,刘改梅,张帆. 蒙宁交界区地震震源深度的对比分析. 中国地震. 2017(02): 290-300 .  百度学术
百度学术
32. 王鹏,郑建常,李铂. 基于PMC方法的山东省测震台网监测能力评估. 地球物理学进展. 2016(06): 2408-2414 .  百度学术
百度学术
33. 宋秀青,游秀珍,刘芳,刘双庆,朱元清. 区域地壳速度模型对准确测定地震参数的重要性研究. 华北地震科学. 2016(02): 27-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
34. 梁莹,张立丰,李惠. 内蒙古赤峰市金厂沟梁镇中学水温上升变化的调查分析. 华南地震. 2016(01): 108-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
35. 蒋长胜,房立华,韩立波,王未来,郭路杰. 利用PMC方法评估地震台阵的地震检测能力——以西昌流动地震台阵为例. 地球物理学报. 2015(03): 832-843 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: