A finite element analysis method for the numerical simulation of characteristic earthquakes: Case study based on the Longmenshan fault zone
-
摘要: 本文构建一种应用有限元开展特征地震数值模拟的新方法, 并以龙门山断裂带中段的浅层构造和动力学机制为背景, 研究了平行逆冲断层分布格局对区域地震活动性的影响. 结果表明, 从断层活动相互影响的角度看, 包含3条平行逆断层的断裂带的整体地震活动性并不适用严格周期的特征地震模型, 当断层间距在20 km以下时, 随着断层间距的缩短, 对单条断层应用特征地震模型的适用性会逐渐降低. 龙门山断裂带中段的模拟计算结果显示, 后山断裂的地震活动相对独立, 区域活动性和中央断裂的断层活动很可能不适用严格周期的特征地震模型.Abstract: This paper constructs a finite element analysis (FEA) method for the numerical simulation of characteristic earthquakes, based on the wide-accepted knowledge of the shallow crustal structure and dynamic boundary conditions at the middle part of the Longmenshan fault zone. The influence of parallel thrust faults on regional seismic activity is focused on and simulated with this FEA model. The results show that the characteristic earthquake model with strict recurrence interval is not suitable for the entire fault zone which contains three parallel faults. When the distance between the faults is less than 20 km, the applicability of the characteristic earthquake model to each single fault is attenuated with the distance between the faults decreasing. The results based on the distribution pattern of the profile in the middle of the Longmenshan fault zone reveal that seismic activity of the back range fault is relatively independent, and the characteristic earthquake model with strict recurrence interval is not suitable for the entire fault zone and the central fault.
-
引言
2008年汶川MS8.0地震发生在龙门山断裂带,使龙门山地区地震活动性研究重新受到重视(闻学泽等,2011). 龙门山断裂带中段主要包含汶川—茂汶断裂(后山断裂)、 映秀—北川断裂(中央断裂)和灌县—江油断裂(前山断裂). 这3条主干断裂自西向东近乎平行展布,总体走向N45°E,倾向NW(邓起东等,1994),其平面示意如图1所示. 汶川震后的地震活动性研究集中于两方面,一方面是历史地震活动整理及关联,从青藏高原东北缘和板块边界的视角探讨龙门山地区的地震能量积累和释放规律(闻学泽等,2009,2011),另一方面是以北川—映秀断裂上M8左右强震为对象的特征地震及其复发间隔研究(张培震等,2008; Shen et al,2009; Wang et al,2011). Ran等(2013)通过在映秀开挖探槽发现,在过去6 000年内显示有包括汶川MS8.0地震在内的3次垂直错动量相近的地震事件,表明汶川地震具有原地复发特征地震的可能,并估计大地震的平均复发间隔在3 000年左右. 对于龙门山断裂带区域地震活动规律与其中单条主干断层的地震活动规律之间的联系和影响,目前尚缺乏讨论,只是笼统地认为可把龙门山断裂带视为一个孕震系统,汶川地震很可能不仅是汶川发震断层的释放,而是整个龙门山断裂带的一次释放(张培震等,2008).
地震活动性统计分析目前主要有两类模型: 一类是概率统计模型如G-R经验公式(Gutenberg,Richter,1954),认为地震发生在有分形结构的自相似系统上,可用自组织临界状态来解释(Bak,Tang,1989); 另一类是特征地震模型(Schwartz,Coppersmith,1984),认为很多成熟的单条断层或断层段在长期活动过程中发生准周期规模相近的重复地震事件,统计经验公式更适用于包含多条断层的较广阔区域(Wesnousky,1994). 根据大地震复发间隔的不同,可分为严格周期的特征地震模型和各类准周期的特征地震模型,大部分特征地震是准周期特征地震,其复发间隔需要应用概率模型来描述(Working Group on California Earthquake Probabilities,1995). 对于特定区域,研究特征地震模型能否描述其中单条断层的地震活动特征以及多断层的分布格局对区域地震活动性的影响,显然具有重要意义. 以单条断层应用特征地震模型为基础的区域地震活动性数值模拟在很多断裂带上取得了研究成果(Thomas,Rockwell,1996; Robinson,Benites,2001),这些数值模拟主要利用静应力变化量来处理断层间的相互作用(Okada,1992; Stein,1999). 由于其模型与计算上的不便,应用有限元力学计算相对较少(Rice,1993).
本文尝试构建一种应用有限元开展多断层特征地震数值模拟的新方法,并结合龙门山断裂带的动力学背景,探讨平行逆冲断层分布形态对区域地震活动性的影响,以及龙门山断裂带区域地震活动规律与其中单条主干断层地震活动规律之间的可能联系.
1. 数值模型
龙门山断裂带中段在垂直于断层走向的方向上受到巴颜喀拉块体的正面挤出压力,以大型陆内逆冲为主要特征(唐荣昌,韩渭宾,1993; 邓起东等,1994). 目前龙门山断裂带中段逆冲动力学机制的数值模拟一般使用平面应变模型(朱守彪,张培震,2009; 张竹琪等,2010),因此本文以图1中虚线方框范围内的3条主干断裂的逆冲破裂滑动为主要研究对象,应用平面应变假设,建立有限元数值模型. 该模型的几何参数和边界约束等如图2所示. 其设计依据如下:
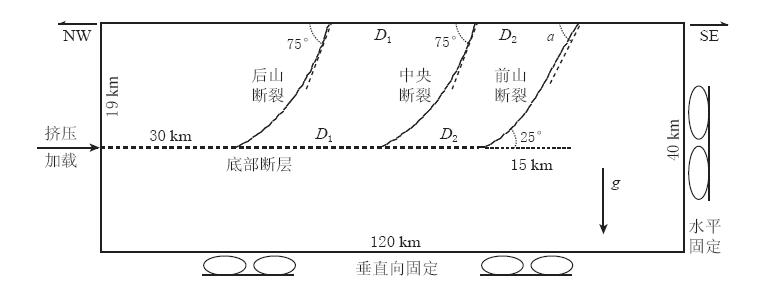
![]() 图 2 龙门山断裂带中段深部构造剖面有限元几何模型 D1,D2分别为后山断裂与中央断裂、 中央断裂与前山断裂之间的距离; ∠a为前山断裂的近地表倾角. 模型为龙门山断裂带中段垂直剖面,模型长度为120 km,自地表至底部40 km.模型南东侧固定水平自由度,40 km深度下边界固定垂直自由度Figure 2. Geometry of the profile in the middle of the Longmenshan fault zone used for the finite element model D1 is the distance between back range fault and central fault,D2 is that between central fault and range front fault,∠a is the dip of the front fault at the crustal surface. The model is for a vertical profile cross Longmenshan fault zone with 120 km long and 40 km depth. The SE end is fixed in horizontal direction and the depth end is fixed in vertical direction
图 2 龙门山断裂带中段深部构造剖面有限元几何模型 D1,D2分别为后山断裂与中央断裂、 中央断裂与前山断裂之间的距离; ∠a为前山断裂的近地表倾角. 模型为龙门山断裂带中段垂直剖面,模型长度为120 km,自地表至底部40 km.模型南东侧固定水平自由度,40 km深度下边界固定垂直自由度Figure 2. Geometry of the profile in the middle of the Longmenshan fault zone used for the finite element model D1 is the distance between back range fault and central fault,D2 is that between central fault and range front fault,∠a is the dip of the front fault at the crustal surface. The model is for a vertical profile cross Longmenshan fault zone with 120 km long and 40 km depth. The SE end is fixed in horizontal direction and the depth end is fixed in vertical direction1)地壳内的断裂面视为已存在的缺陷,应用带有摩擦机制的接触单元来描述(Wriggers,2006). 地震地质资料显示,龙门山断裂带20 km深度附近的地壳内分布有近水平向的低速低阻层(滕吉文等,2008; 朱介寿,2008; 刘启元等,2009),而汶川地震初始破裂点最深的位置可能也在19 km左右(刘启元等,2008),因此,本模型中以19 km深度为界,把断裂面划分为浅部断层和底部断层两个部分.
2)深度在19 km以上的断裂面设定为浅部断层,断层破裂受静摩擦限的控制,即静摩擦系数大于动摩擦系数,只有当剪力超过静摩擦力,断层才会开始破裂滑动. 在断层滑动中,应用带有破裂滑动状态和速率参数的库仑摩擦模型,即实际滑动摩擦系数的大小与断层处于闭锁或滑动的何种状态,以及断层面两侧地壳体相对速度的大小有关. 以两端点带切向角度(分别对应断层的近地表倾角和基底倾角)的样条曲线来模拟龙门山断裂带断层在地壳中上陡下缓倾角渐变的展布特征(张伟等,2012). 综合已有资料和研究结果(李勇等,2008; 徐锡伟等,2008; 杨光等,2012; 张伟等,2012),本模型近地表倾角设为75°,基底倾角设为25°.
3)深度大于19 km的断裂面设为底部断层. 由于龙门山地区底部断裂面在地壳中接近水平向展布(滕吉文等,2008; Wang et al,2011),因此这部分断层的产状以水平向的直线来模拟. 底部断层的摩擦机制简化设计为静摩擦系数、 动摩擦系数与实际滑动摩擦系数相同,即断层模型破裂中没有静摩擦限.
为探讨平行断层的分布格局与地震活动特征的关系,将图2中的前山断裂与中央断裂、 中央断裂与后山断裂的距离D1,D2和前山断裂的近地表倾角∠a选取11种组合,即针对如下11个模型进行计算:
1)D1和D2分别选取30 km/30 km、 25 km/25 km、 20 km/20 km、 17 km/17 km、 13 km/13 km、 10 km/10 km、 7.5 km/7.5 km和5 km/5 km.
2)针对小鱼洞至擂鼓段3条主干断层地表破裂带距离(唐荣昌,韩渭宾,1993; 徐锡伟等,2008),选取D1/D2为27 km/12 km. 汶川地震汉旺白鹿段地表破裂倾角约55°(杨光等,2012),因此对27 km/12 km模型,∠a=75°或55°,模型代号设为27/12/75°和27/12/55°.
3)最后构建一个单断层模型,该模型仅有中央断裂一条断层,其它与图2一致.
模拟计算中,对模型的介质参数及边界条件等设计如下:
1)由于龙门山地区的地壳厚度大于40 km,并且是具有较高强度的变质杂岩体(宋鸿彪,1994),因此本文实验中把模型的深度设定为40 km,使实验对象保持在中上地壳范围 内,岩体材料设定为弹性. 参考龙门山地区地壳介质的参数资料(宋鸿彪,1994; 滕吉文等,2008; 朱介寿,2008),弹性模量设定为7×104 MPa,密度为2.7×103 kg/m3,泊松比为0.2,重力加速度为9.8 m/s2.
2)库仑模型摩擦本构关系μ=μ0+μ0(a-1)e-bV中,μ为滑动时的实际摩擦系数,μ0为完全滑动时的理想摩擦系数,aμ0为静摩擦系数. 综合岩石摩擦试验结果(陈颙等,2009)、 龙门山断裂带已有资料及研究成果(朱守彪,张培震,2009; 何昌荣等,2011),本文试验取a=1.05,μ0=0.2; V为接触面相对速度,b为衰减系数; 基于静力分析,本文没有对时间积分,b值对结果影响很小,经试验b=100即可使断层状态平缓切换; 底部断层摩擦系数简化为μd,取μd=0.2.
3)巴颜喀拉块体对龙门山断裂带长时间的挤压通过水平向固定模型南东侧、 水平挤压北西侧使得模型水平缩短来描述. 施加重力后,模型水平挤压缩短采取分步加载,每步加载1 m,待调整稳定后,再进入下一步,最终各模型在水平挤压加载下缩短2 400 m(加载到2 400 m时,模型整体水平应变约为2%,已超出一般介质的弹性范围,属于极限情形). 巴颜喀拉块体朝南东方向的挤出导致200多千米边界带上的水平向缩短3.5—6 mm/a(闻学泽等,2011). 取水平向缩短为5 mm/a,则1 m的北西侧挤压加载量对应的演化周期为200年.
对有限元模型进行边界加载后,根据断层接触状态变化和最小滑动标准(0.05 m),单断层模型共发生82次破裂,其余10个模型均发生240次左右的单条断层破裂. 对每次破裂按照M0=G · LM · ∫FS · LFdL计算标量地震矩. 式中,切变模量G为2.92×104 MPa,S为沿断层倾向的滑动量分布,LF为沿倾向的断层长度. 沿断层走向破裂长度LM与每次破裂的规模有关,考虑到这种相关对本文结果没有实质影响,为使结果更直观,参照汶川破裂情形,LM统一简化为200 km. 底部断层上的滑动量较小,为简化计算,本文不予统计.
2. 单断层模型结果与方法验证
单断层模型计算得到的断层模拟破裂的地震矩和孕震时间如图3中左上角的小图所示. 由于接触面的弹性滑动设置为1%(Wriggers,2006),因此在模型加载初期,断层面上会有一定的弹性滑动量来调节加载变形,使得破裂孕育间隔出现扰动. 随着加载到一定程度,断层面达到弹性滑动极限,只能通过破裂来释放滑动量. 可以看到,随后断层出现准周期破裂,每次破裂的地震矩、 孕育时间随挤压加载量线性增大. 这种现象是由于弹性材料在持续加载下应力不断增大所致. 引入黏弹性材料虽可实现应力松弛,但也会带来新的问题. 由于目前地震前后的地壳应力演变周期并不明确,因此应力松弛的目标难以确定; 另一方面,要实现预定的地壳应力区间需要材料属性和加载过程的诸多人为控制,而且还将导致大尺度的线性蠕变和上层地壳破裂行为的畸变(王芝银,李云鹏,2008). 因此,本文通过线性回归来消除由于应力累积导致的地震矩和孕育时间的线性增长,以回归拟合值作为模拟地震的特征地震矩和复发周期,以回归的残差标准差作为特征地震矩和复发周期的误差,以回归的相关系数来考察模型断层在持续挤压下破裂的行为特点.
取回归区间见图3小图中的虚线框所示(对应模型整体水平应变在0.5%—1.1%的合理范围),断层破裂的地震矩、 孕震时间和相应的回归直线如图3所示.
汶川地震的标量地震矩约为9.82×1020 N · m(Wang et al,2011),以逆冲为主. 本文模型仅考虑逆冲分量,因此目标地震的标量地震矩取为6×1020 N · m. 在单断层模型的地震矩拟合线上,6×1020 N · m对应的挤压加载量为820 m,此时模型整体水平挤压应力约为480 MPa,处于10 km深度地壳水平应力的合理范围(Zoback et al,1985). 本文以挤压加载量820 m为汶川地震发生时的宏观地壳应力,单断层模型模拟的汶川地震模拟结果如图3所示.
单断层模型地震矩和破裂孕育时间与挤压加载量的线性相关系数分别高达0.99和0.97,而回归的残差标准差则分别低至0.35×1020 N · m和80 a,表明本文方法具有合理性. 汶川地震的复发周期研究结果表明,映秀—北川断裂上MS8.0地震的复发间隔应该在2 000—10 000 a之间(张培震等,2008; Burchfiel et al,2008; Shen et al,2009; Ran et al,2013). 本文单断层模型拟合的汶川地震破裂复发周期为4 105 a,处于现有研究结果的密集区间,验证了本文模型和方法的有效性. 对各模型均采用上述方法,得到了相应的挤压加载量820 m时模拟地震的地震矩和破裂复发周期.
3. 平行断层分布格局对孕震周期和破裂释放的影响
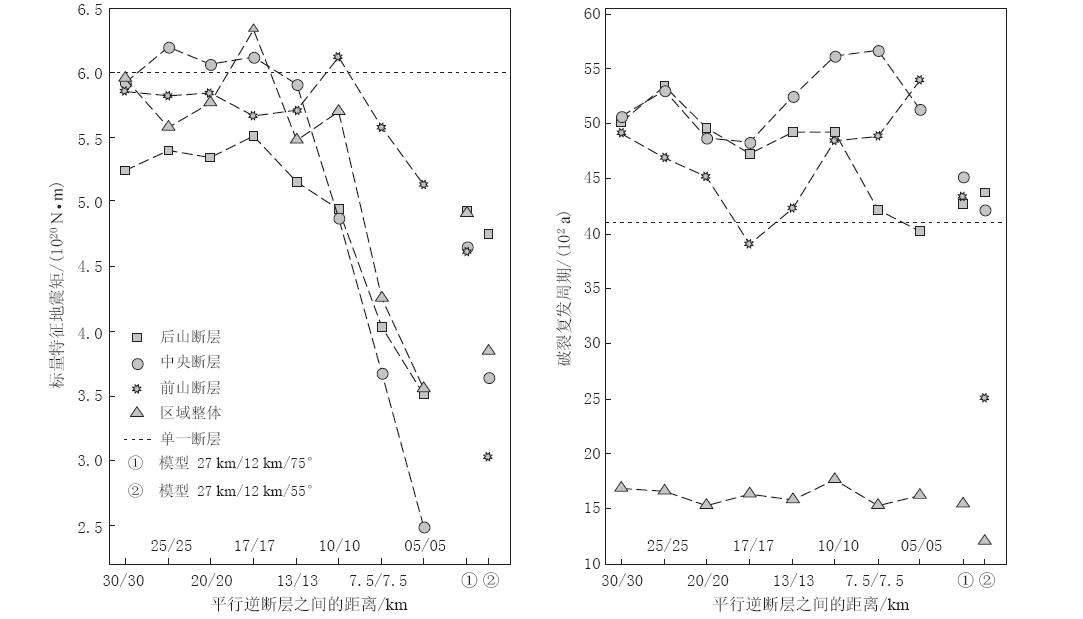
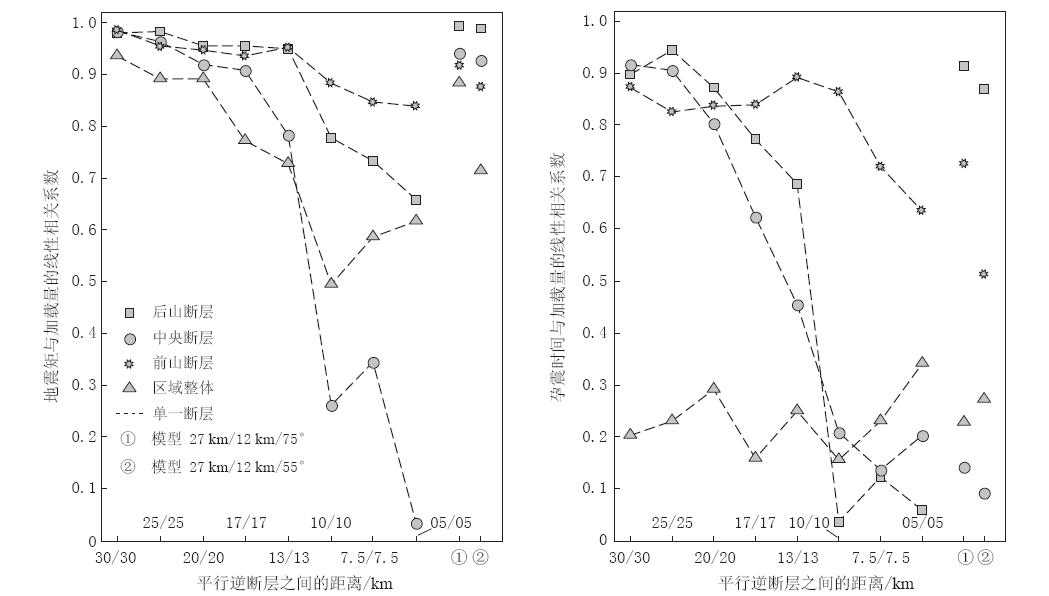
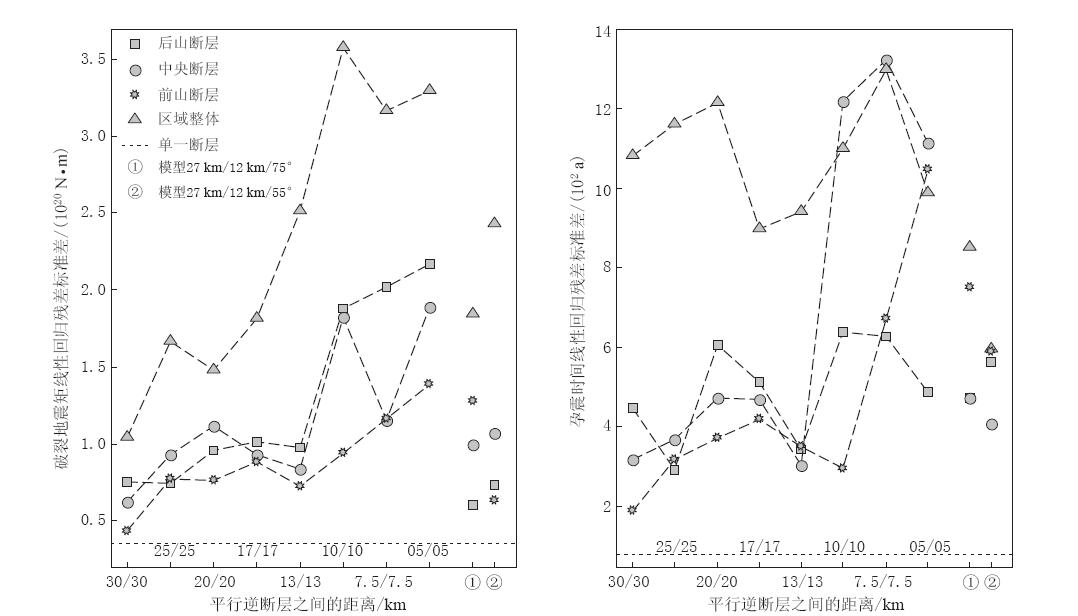
各模型单条断层和区域模拟破裂的特征地震矩和破裂复发周期如图4所示,相应的线性相关系数及回归残差标准差分别如图5和图6所示. 可以看出,当断层间距在20 km以上时,单条断层的地震矩和破裂复发周期均比较稳定,与挤压加载量显著线性相关,回归残差也处于比较低的水平. 当断层间距在17 km以下时,随着断层间距的缩小,单条断层的破裂释放地震矩有显著变小的趋势,地震矩和复发周期与挤压加载量的线性相关程度也显著下降,拟合残差总体上有所增大.
这3种变化最终都会导致大幅偏离单断层模型的结果,其中前山断裂的变化相对平缓,中央断裂变化最大.
与挤压加载量的线性相关程度降低、 回归残差变大,表示断层的破裂行为与宏观动力学机制之间的规律性降低,说明此时单条断层的破裂行为不再只受宏观动力学机制的控制. 在模拟中,与单断层模型相比,多断层模型增加的因素就是单条断层活动对周边断层的影响. 因此可以认为,这种偏离单断层模型的变化,是来自于断层活动之间的相互影响. 模拟结果表明,对于本文所讨论的平行逆冲断层,断层间距是断层活动之间相互影响的控制因素,断层间距越小,相互影响越大.
从计算结果看,当断层间距在20 km以上时,断层之间的相互影响较小,对单条断层自身破裂行为的干扰作用有限. 3条断层在空间上串联承受挤压,但是破裂表现却是并行形式,每条断层的破裂释放与单独承受相同挤压缩短时的表现基本一致,即按照自身节奏准周期发生规模相近的破裂释放. 这表明,此时单条断层可以适用特征地震模型.
当断层间距缩小到17 km以下时,单条断层的破裂与释放开始受到周边断层活动影响的干扰,破裂节奏和地震矩释放量逐渐失去规律. 随着断层间距的逐步缩小,这种干扰越来越大. 该结果表明,此时在多断层系统中的单条断层上开始逐渐不适用特征地震模型,断层间距越小,其适用性越低.
区域复发周期的计算结果显示,无论断层间距如何变化,区域复发周期均稳定在1 000—2 000 a,且线性相关程度低、 残差大. 即使当断层间距在20 km以上,区域内3条断层的复发周期均有较强的规律,区域破裂复发周期依然是低相关、 高残差. 由此可见,即使区域内每条断层都适用严格周期的特征地震模型,包含3条断层的区域地震活动性也无法用严格周期的特征地震模型来描述,其复发间隔需要应用概率模型. 该结论与已有研究结果(Wesnousky,1994; Ben-Zion et al,2003)基本一致.
4. 龙门山断裂带中段模拟结果
针对龙门山断裂带中段的两个模型计算结果已在图4,5和6中给出. 可以看到,总体上该结果介于20 km以上模型与17 km以下模型之间.
两个模型的计算结果均显示,后山断裂的特征地震矩与复发周期比较稳定且相关性好,而中央断裂破裂复发周期与挤压加载量的线性相关程度极低. 这表明后山断裂的活动相对独立,而中央断裂的破裂行为则受到前后两个断裂的极大影响. 该结果与汶川地震的断层破裂情况相吻合(徐锡伟等,2008). 这主要由于后山断裂与中央断裂间距大于20 km,因此断层之间相互影响较小,而前山断裂与中央断裂之间12 km的距离使得断层活动相互影响较大.
前山断裂近地表缓倾角(55°)时的结果与陡倾角(75°)结果相比,前山断裂的地震矩释放与复发周期显著变小,表明前山断裂的强震行为有较大弱化. 该结果显示了前山断裂近地表缓倾角的影响. 在逆冲断层的闭锁积累强震释放的过程中,相对于陡倾角,当断层为近地表缓倾角时,在相同条件下其近地表逆冲闭锁能力就更弱,因此会导致更频繁规模更小的破裂释放(嵇少丞等,2008).
27/12/55°模型的计算结果显示,龙门山断裂带中段的区域破裂孕育时间和中央断裂的破裂孕育时间与挤压加载量之间几乎无线性关系,只能用统计规律来分析. 以600 a分段的区域破裂孕育时间分布比例符合均值μ=1281 a、 σ=741 a的正态分布,中央断裂破裂孕育时间则符合μ=4117 a、 σ=436 a的正态分布,具体分布如图7所示. 结果表明,对于整条断裂带或者中央断裂来说,严格周期的特征地震模型很可能是不适用的,复发间隔需要引入概率模型来进一步讨论.
5. 讨论与结论
本文构建了一种应用有限元开展特征地震数值模拟的新方法. 该方法可以有效地消除应力累积对模型长期破裂演化结果的影响,得到黏滑模式断层以特定地震为目标的模拟特征地震的地震矩和复发间隔. 基于龙门山断裂带中段动力学背景的模拟实验结果验证了该方法的有效性. 该方法的不足在于模拟的目标为特定规模的地震,并不能产生全量级的理论地震目录; 另一个不足在于适用性有限,随着断层间距变大或有空间复杂性,很多计算在现有条件下可能就难以完成.
本文模拟结果表明,在龙门山断裂带中段的构造背景和动力学机制下,包含3条平行逆断层的断裂带地震活动具有如下特点:
1)从断层活动相互影响的角度看,断层间距在20 km以上时,单条断层可以适用特征地震模型; 断层间距在20 km以下时,随着断层间距缩短,单条断层应用特征地震模型的适用性逐步降低.
2)包含3条断层的断裂带,其地震活动性不适用严格周期的特征地震模型,即使3条断层都分别适用严格周期的特征地震模型,断裂带的特征地震复发间隔仍需要用概率模型来描述.
对于龙门山断裂带中段来说,后山断裂的地震活动很可能相对独立,有自身的孕震和破裂节奏,而中央断裂与前山断裂之间相互影响较大. 从断层活动相互影响的角度看,区域活动性和中央断裂的断层活动均难以用严格周期的特征地震模型来描述,前山断裂的近地表缓倾角很可能使得前山断裂的强震行为有所弱化.
特别需要说明的是,一条断层或断层段是否发生特征地震,会受到动力学环境和地震地质等多方面影响(闻学泽等,1994). 本文方法只是从断层活动相互影响的角度来研究考虑,单条断层和区域是否适用特征地震模型,适用特征地震模型并不意味着就会发生特征地震,而如果无法适用特征地震模型,就很难发生特征地震.
本文实验结果对龙门山断裂带的强震灾害预测具有启发意义,但是需要注意平面应变和模拟过程中重要假设所带来结果的应用局限性. 另外,本文主要是讨论平行逆断层分布格局对断层长期行为的影响,因此设计模型时使平行逆断层之间的形态与底部动力学条件尽可能一致. 实际上龙门山断裂带中段3条断层在底部也可能是叠瓦式逆断层构造(Xu et al,2009); 所构造的断层也只是满足龙门山断裂带上陡下缓、 近地表陡倾角的基本特征,并没有讨论各条断层的最可能产状形态. 今后可以结合更多构造信息,进一步讨论龙门山断裂带中段逆断层平行分布的影响.
本文及有关研究工作得到白以龙院士、 甘卫军研究员的建议和修改意见,在此一并表示感谢.
-
图 2 龙门山断裂带中段深部构造剖面有限元几何模型 D1,D2分别为后山断裂与中央断裂、 中央断裂与前山断裂之间的距离; ∠a为前山断裂的近地表倾角. 模型为龙门山断裂带中段垂直剖面,模型长度为120 km,自地表至底部40 km.模型南东侧固定水平自由度,40 km深度下边界固定垂直自由度
Figure 2. Geometry of the profile in the middle of the Longmenshan fault zone used for the finite element model D1 is the distance between back range fault and central fault,D2 is that between central fault and range front fault,∠a is the dip of the front fault at the crustal surface. The model is for a vertical profile cross Longmenshan fault zone with 120 km long and 40 km depth. The SE end is fixed in horizontal direction and the depth end is fixed in vertical direction
-
陈颙, 黄庭芳, 刘恩儒. 2009. 岩石物理学[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社: 343-374. Chen Y, Huang T F, Liu E R. 2009. Rock Physics[M]. Hefei: Press of University of Science and Technology of China: 343-374 (in Chinese).
唐荣昌, 韩渭宾. 1993. 四川活动断裂与地震[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 34-63. Tang R C, Han W B. 1993. Active Faults and Earthquakes in Sichuan Province[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 34-63 (in Chinese).
王芝银, 李云鹏. 2008. 岩体流变理论及其数值模拟[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 30-70. Wang Z Y, Li Y P. 2008. Theory of Rock Rheology and Its Numerical Simulation[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 30-70 (in Chinese).
Wriggers P. 2006. Computational Contact Mechanics[M]. New York: Springer: 356-412.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: