Research on the observation methods and techniques of omni-directional spontaneous electric field
-
摘要: 自然电场是一种物理意义比较明确, 变化(孕震)机理相对明晰的地球物理场, 在矿产资源勘探、 水文地质勘测等领域有着比较广泛的应用, 在地震监测领域也有了多年的探索和实践. 本文在初步研究全方位自然电场观测方法的基础上, 重点分析和讨论了基于全方位自然电场观测技术, 包括一种Pb-PbCl2不极化电极、 多测道高精度数据测量、 网络控制与数据通信等组件和模块的基本原理和技术实现方法, 便携式设计和环境温度适应能力的技术实现途径等, 并对天津市静海地震台的自然电场试验观测系统及观测数据进行了简要介绍和分析讨论. 结果表明: ① 全方位自然电场观测方法能够捕捉到各个方向自然电场及其随时间的变化; ② 自然电场观测技术系统能够配合全方位自然电场观测方法, 在360°范围内开展自然电场及其随时间变化的动态变化测量, 具有较高的观测精度、 较强的抗干扰能力和观测环境适应能力; ③ 天津市静海地震台的试验观测系统记录到了可能与周边水系的季节性变化有关的自然电场全方位变化.Abstract: Spontaneous electric field is a kind of geophysical field with clear physical meaning and variation mechanism, which is used in various domains like mineral resource prospecting, hydrogeologic survey and earthquake monitoring. Based on preliminary study on omni-directional spontaneous electric field observation methods, this paper focuses on the analysis and discussion of spontaneous electric field observation techniques, including a kind of Pb-PbCl2 non-polarized electrode, multi-channel high-precision data measurement, network control and data communication, and technical realization of portable design and environmental temperature adaptability. Finally, it presents a brief introduction and discussion on the observation system and data of the spontaneous electric field at Jinghai seismic station in Tianjin Municipality. The results show that ① omni-directional spontaneous electric field variation with time could be captured by this method; ② measurement of electric field and its temporal change in 360° azimuthal range could be carried out by using the spontaneous electric field observation techniques, which have high observation precision, strong ability of anti-interference and strong environmental adaptability; ③ multi-directional changes of spontaneous electric field, which were possibly related to seasonal changes of the surrounding water, were recorded by the test observation system of Jinghai seismic station.
-
Keywords:
- omni-directional /
- spontaneous electric field /
- observation method
-
引言
地电场是由固体地球内部和外部的各种非人工电流系统与地球介质相互作用所产生的分布于地表的电场,可分为大地电场和自然电场(钱家栋等,2004; 钱家栋,2010). 其中,大地电场的场源来自地球外部的各种电流体系,在地球表面的有限区域内可视为似平面波(李金铭,2005); 自然电场(又称自然电位)由地下矿体和电解质与周围介质之间以及地下岩石结构体之间的物理化学作用产生.
一般情况下,自然电场具有相对稳定性,但也会由于局部性的地下水系、 裂隙的变化,产生时间和空间上的剧烈变化. 根据物探电法中对自然电场及其变化特性的研究分析结果,自然电场的这种剧烈变化与地下水活动和运移等有密切的关系,主要是由地球自身的运动形成液体的对流(含热对流),以及在日潮、 月潮和电磁潮的共同作用下产生的结果(莫承彬,陈忠献,1995). 目前认为,地震孕育过程中最可能产生局部自然电场的机理是动电效应(刘耀伟等,2004),也可能由地下水位变化及断层活动产生的过滤电动势引起(钱复业,赵玉林,2005).
影响自然电场的主要因素包括地下结构体的物理属性、 破碎断裂带的规模与展布、 地下水系的发育程度、 岩石应力的分布与强度和潮汐力的外力作用(谭大诚等, 2010,2011)等,由此产生的自然电场局部非均匀性和各向异性变化特征比较明显. 我国地震监测领域对自然电场的研究可追溯到20世纪60年代,主要利用地电阻率观测中的自然电位Vsp数据,一般在两个方向进行观测,每天或每小时产出1组数据; 始于20世纪90年代的数字化地电场观测与研究以大地电场及其随时间变化为主,其中包含有自然电场的成分,观测方位也大多局限于两个(正交的)观测方向. 由于观测方法的这种局限性,基于地电阻率观测和地电场观测中获得的自然电场数据,尚不能全面反映自然电场的这种局部性各向异性变化特点.
本文借鉴物探电法中的“环形梯度法”(“8”字型观测法)(王俊业,2002),引入一种能够应用于地震监测的新型自然电场观测方法,即“全方位自然电场观测方法”; 并开展一种能够实现该观测方法的小型化、 低功耗和较强环境适应能力的自然电场观测技术系统研究,以期能够对地震危险区和地震现场等特殊的野外环境开展无人值守观测,最大限度地捕捉自然电场多方位变化信息.
1. 全方位自然电场观测方法
1.1 自然电场分量测量
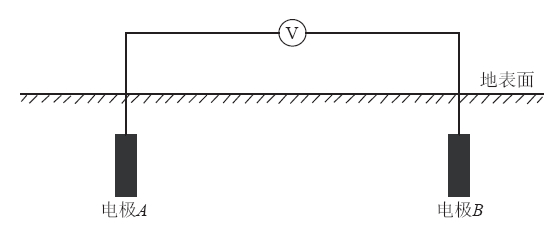
自然电场分量测量的基本方法为,在指定方向、 按照一定的电极极距,布设如图 1所示的观测装置,测量该装置下两个电极A和B之间的电位差V. 该电位差V中包含的物理量包括天然的大地电场和自然电场成分,也包含了可能存在的电极极化电位和由于环境等产生的干扰电场(式(1)).

式中,Vt表示大地电场,Vsp表示自然电场,Vp表示极化电位差,Vn表示其它干扰电场.
为了从图 1所示的测量方法得到的电位差V中获得自然电场Vsp及其变化信息,需要从观测得到的原始数据V中滤除大地电场Vt变化,并消除极化电位差Vp以及干扰电场Vn的影响. 其中,当使用极化电位差较小的不极化电极时,在误差允许的范围内,极化电位差Vp的影响可以忽略不计,也可以通过同点多电极对比观测的方式对电极的极化电位的影响进行识别和处理; 干扰电场Vn的影响则可以通过选址规避(钱家栋等,2004)和数据滤波等方式进行抑制和消除.
在消除了式(1)中所示的极化电位差Vp、 干扰电场Vn的影响的情况下,式(1)可简化为式(2),其中仅包含了天然的大地电场和自然电场的成分

大地电场的典型变化形态包括地电日变化和地电暴等. 资料分析表明,地电日变化以12 h,24—25 h和8 h为中心的周期成分最强,几小时、 几分钟的短周期成分也很清晰; 地电暴的高频变化比较丰富(叶青等,2007). 依据大地电场的这种周期性变化特点,可以通过滑动平均(等效低通滤波)、 算术平均(日均值等)等方法将式(2)中的大地电场变化成分滤除,获得自然电场及其变化. 其中,利用滑动平均从观测数据V中提取自然电场变化的计算公式如式(3)所示(席继楼等,2009):

式中,Vi表示当前测量数据之前第i个V测量数据,i=N-1,N-2,…,2,1,0(单位: mV); N为参与计算的数据总数,不少于24 h之内的所有测量数据个数.
1.2 全方位自然电场观测
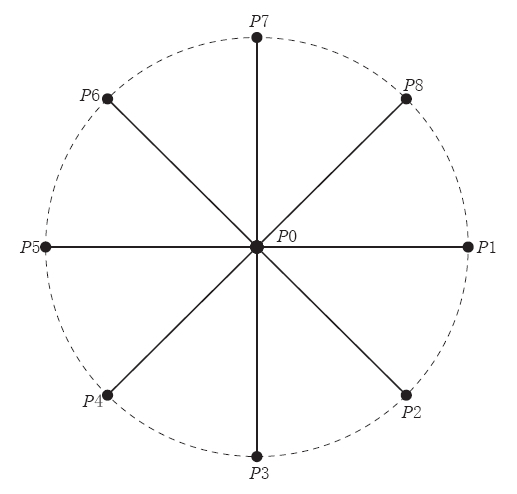
全方位自然电场的测量原理如图 2所示. 以观测区域的中心点O为基准点,在360°范围内的多个方向(不少于8个)上按照图 1所示的方法埋设电极(P1—P8)和布设线路,测量和计算在对应方向上布设的电极(P1—P8)与基准点电极P0之间的自然电场分量值Vjsp. 其中,在基准点(公共点O)和其它电极埋设处可以埋设一组(不低于2只)电极,用于检测和识别测量电极的极化电位的可能变化.
利用图 2所示的“全方位”自然电场观测方法,可以同步测量得到多个方向上自然电场及其随时间的变化. 当获得了每一个方位的自然电场分量值及变化数据以后,可以用极化图的形式描述该测量区域的自然电场在360°范围内的动态变化,从而获得自然电场的最大变化方位和变化信息.
2. 自然电场观测技术研究
在对自然电场观测方法进行初步研究的基础上,开展了能够实现这种全方位观测的自然电场观测技术系统的研究工作,主要包括一种高稳定性的Pb-PbCl2不极化电极研究,高精度多通道同步测量技术研究,观测数据网络通信技术研究以及环境适应能力研究等.
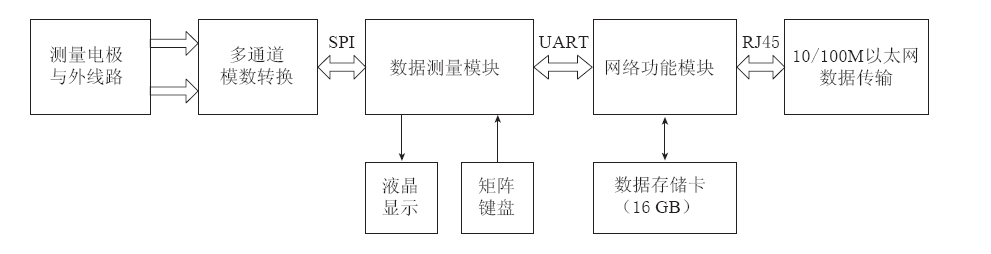
自然电场观测技术系统的总体功能框架结构如图 3所示,其中测量电极采用一种基于Pb-PbCl2技术实现方案的不极化电极; 测量电极与测量主机之间通过绝缘铜导线连接; 测量主机采用多模块分体式结构(双CPU结构)设计,主要完成自然电场数据的采集、 调理、 转换、 处理和存储等,并通过互联网或局域网远程传输自然电场观测数据.
2.1 一种Pb-PbCl2不极化电极
测量电极是连接大地和金属导线的导体,主要功能是承载离子导体与电子导体之间的电压(流)传导,是自然电场观测中的关键组件. 目前在地电观测中一般使用金属铅电极和Pb-PbCl2固体不极化电极. 其中,金属铅电极由于直接与土壤大面积接触,容易产生比较大的极化电位,且当周围土壤介质条件(如温度、 湿度、 电解质浓度等)发生改变时,该极化电位易发生较大波动; 不极化电极的极化电位差比较小(1 mV以下),可以进行固态封装,在携带、 安装和使用方面有较大的灵活性,目前国际上在这方面的研究比较多. 测量电极的极化稳定性(定点观测)和可维护性(流动观测)则是实现野外环境下,特别是在应急现场或流动测量的情况下,开展自然电场观测的重点要素.
研究表明,影响不极化电极使用状态稳定性的主要因素包括如下几个方面: ① 过渡介质(溶液)电解质浓度的稳定性; ② 电极内阻的稳定性; ③ 电极与大地之间接触电阻的稳定性; ④ 受环境因素影响的稳定性等(宋艳茹等,2011).
不失一般性,我们在进行技术实现时,采用了电化学性质比较稳定且国际上应用比较广泛的Pb-PbCl2技术实现方案(图 4). 在多次试验的基础上,通过改变金属铅电极(铅芯)的几何结构和表面处理方法,调整过渡混合介质(溶液)的添加电解质比例和酸碱度等技术措施,提高电极极化电位的一致性,达到在组合使用时降低电极极化电位差的目的. 同时,为了保证电极自身工作状态的稳定性和可维护性,我们有针对性地设计了一种分体式可拆解结构,带引线和金属极芯的电极顶盖、 全向接触型电极底部装置与电极主体之间均可利用螺纹进行连接和自由拆解,方便制作、 使用和维护(实用新型专利一种固体不极化电极: 中国,ZL2010-2-0257982.X[P]. 2011.).
通过上述途径实现的不极化电极,在实验室条件下(放置在100%饱和NaCl溶液中)测试的基本性能指标如下: ① 频率范围DC—100 kHz; ② 极化电位差≤0.2 mV(优化组合可达0.1 mV); ③ 短期稳定性(24 h)≤0.1 mV; ④ 极化噪声(60 s)≤0.01 mV; ⑤ 线性度误差≤0.1%; ⑥ 电极内阻≤100 Ω. 该测试结果不低于国内外目前公开的不极化电极主要性能指标(宋艳茹等,2011).
2.2 多测道高精度自然电场测量
图 3中所示的“数据测量模块”主要完成多通道高精度自然电场测量和数据采集工作. 该模块通过对测量电极及外线路捕捉和传递的自然电场信号进行调理、 模拟数字转换、 测量控制、 数据缓存、 数据输出等,实现自然电场信号的数字化测量.
“数据测量模块”的核心器件和电路主要包括8 bit 片上系统(system on chip,简写为SOC)中央控制器件C8051FXX,24 bit ∑-Δ模数转换(analog to digital converter,简写为ADC)器件AD771X,+5 V高精度模数转换基准源,I2C接口高精密可自充电时钟芯片SD200X,32 kB高集成度大容量缓存器件61LVXXXX,以及多种编码解码逻辑器件等. 其中,C8051FXX集成了多种总线(如SPI,I2C,UART,PCA等)、 控制器(Port I/O,Time等)、 存储器(ROM-Flash,RAM-Flash,SRAM等)和其它混合信号系统; AD771X是一款适用于低频测量应用的完整模拟前端器件,它直接从传感器接收微弱的低电压信号,经过24 bit ∑-Δ模数转换以后,利用与SPI,QSPI和MICROWIRE完全兼容的串行接口输出数字信号,同时通过该串口接收主控软件指令,完成增益设定、 梳状滤波频率设置及测量通道切换等操作; 数据缓存包括内置RAM和外部扩展SRAM两部分存储器件,RAM用于保存临时数据,SRAM配置了掉电保护功能,可以存储较长时间的数据,SRAM中保存经过计算和处理以后的自然电场观测数据(十六进制补码格式),保存在SRAM中的数据在一个数据测量周期结束以后,通过内部UART接口传送至“网络功能模块”.
由于“数据测量模块”属于模拟数字混合电路,为增强观测数据的稳定性,在模数转换电路与主控电路之间专门设置了光电隔离器件,实现无物理(电气)连接情况下的逻辑电平转换连接,用于测量控制信号的传递,以及模拟数字转换电路测量数据的读取等. 通过光电隔离器件的连接,模拟电路与数字电路的地信号完全分隔,可以较好地抑制来自外环境的接地共模干扰,以及来自数字电路本身的背景噪声干扰等(席继楼等,1999).
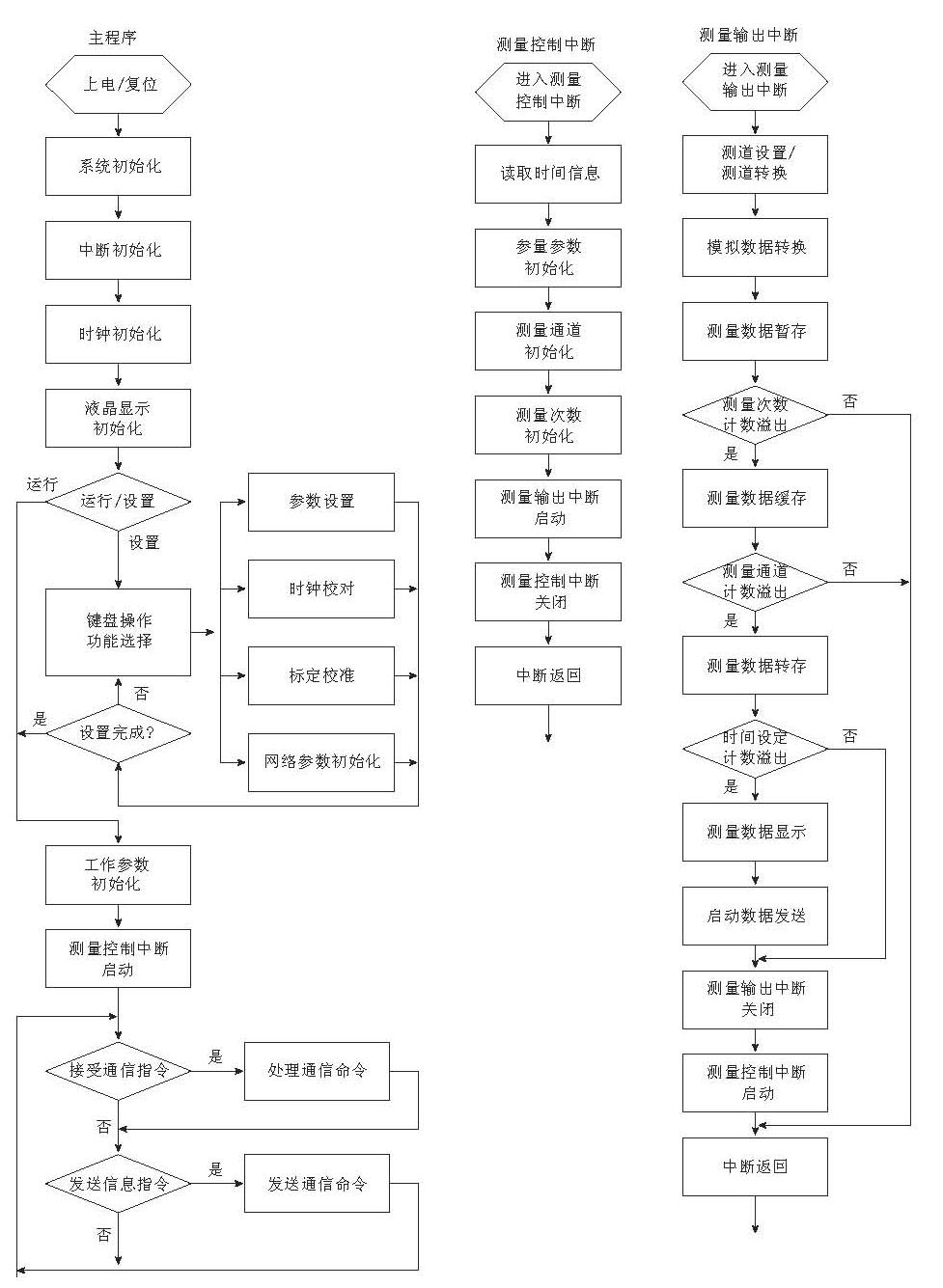
“数据采集模块”的控制设计基于Keil7.0的C51开发平台编写. 该控制软件借鉴和融合了多进程的编程思想,将关键操作和控制单元分解为几个互相独立的功能模块,软件框图如图 5所示. 其中,“主程序”主要是完成系统、 参数、 中断、 时钟、 液晶显示等功能组件的初始化,并根据预设的信号指示,实现多进程之间的调度; “测量控制中断”由外部时钟提供中断源,每秒钟中断启动一次,该中断主要完成测量参数的设置,并启动“测量输出中断”程序,在“测量输出中断”启动期间,“测量控制中断”予以关闭; “测量输出中断”由ADC提供中断源,当ADC完成一次模拟数据转换后,发出转换完成信号,由“测量输出中断”程序完成数据的读取、 暂存、 缓存和转存,并根据“测量控制中断”程序设置的指示参数,在测量完成后关闭“测量输出中断”,重新开启“测量控制中断”,等待下一次“测量控制中断”信号.
当指定时间段(通常为1分钟)内各个测道的数据转换完成后,由图 5中所示的“测量输出中断”程序启动数据发送指令,将这一时间段的数据发送到“网络功能模块”,由该模块做进一步的处理、 存储和网络传输等.
在实验室环境条件下,测试得到的主要性能指标如下: ① 观测精度(最大允许误差)不低于0.1%R±0.1 mV; ② 测量分辨力优于0.01 mV; ③ 测量范围±1000.00 mV; ④ 输入电阻不低于20 MΩ; ⑤ 工频串模抑制比不低于80 dB; ⑥ 工频共模抑制比不低于140 dB; ⑦ 测量通道12个(8个主测道、 1个备用测道、 3个辅助测道); ⑧ 采样率不低于每分钟12次/道.
2.3 网络控制与数据通信
图 3中所示的“网络功能模块”主要完成自然电场测量数据的转换处理、 网络传输以及其它控制功能. 该模块中主要采用了32 bit XScale PXAXXX系列先进精简指令集处理器(advanced RISC machine,简写为ARM)芯片,配合SDRAM、 NAND-Flash、 NOR-Flash、 ROOT-ROM、 10/100M以太网控制器、 PCMICA驱动、 UART驱动等外部设备,组成一个功能比较完整的微处理系统. “网络功能模块”能够实现对“数据测量模块”上传的自然电场测量数据(12个测道,十六进制补码格式,每秒12个采样点)进行格式转换、 干扰处理、 大容量数据存储(最大支持16 GB)、 网络数据服务等功能. 它同时配备了不掉电时钟(RTC)、 看门狗电路(WDT)、 防静电保护(ESD)等电路,增强系统工作的可靠性; 预置的USB接口、 LCD/VGA接口等,方便程序开发,增强系统的可维护性.
PXAXXX系列ARM控制器能够兼容ARM7和ARM9的指令系统,支持WinCE和Linux操作系统和高级语言编程等. 我们采用WinCE操作系统作为控制平台,通过内嵌的TCP/IP协议栈完成各种网络通信和控制功能. 其中,通过服务器端网络控制软件,能够实现观测数据的在线准实时命令传输,可以兼容和实现地震前兆台网网络通信协议规定的相关通信和控制功能; 内置的WEB服务器功能,能够部分实现HTTP协议转换和处理;内置的FTP服务器能够实现大容量存储数据的下载,完成服务更新程序的上传等.
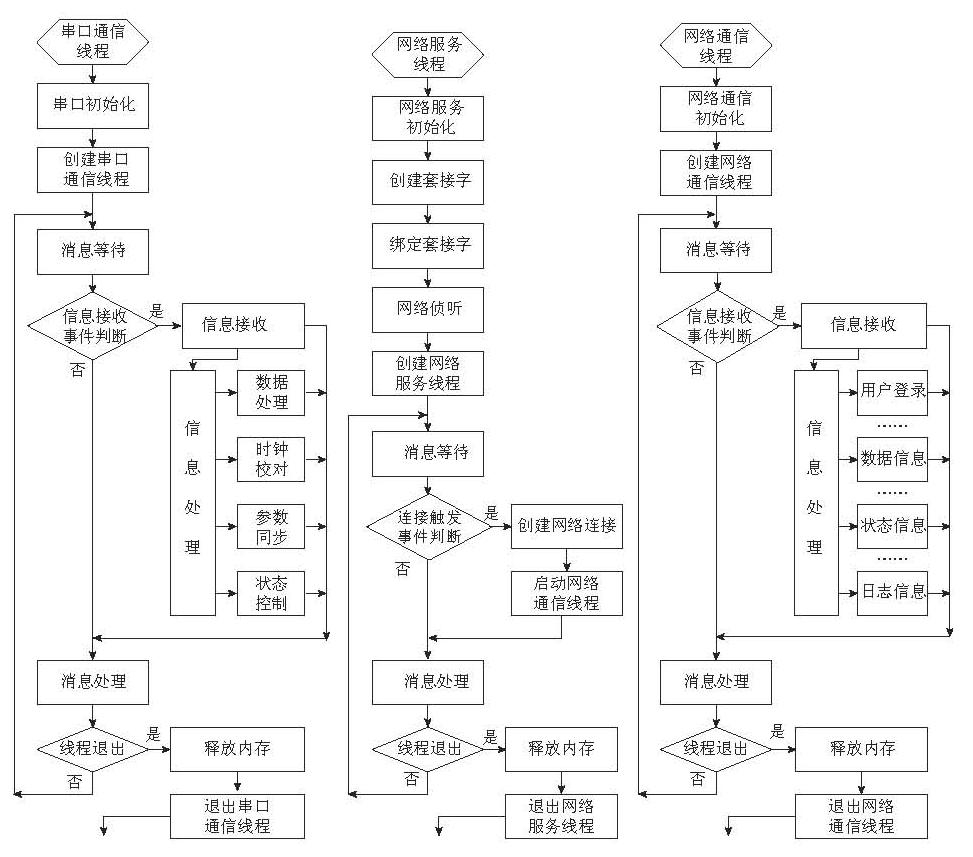
“网络功能模块”的控制和处理软件,在基于ARM架构的WinCE平台下,利用VS2005开发环境下的VC++语言进行编写. 按照多线程编程方法,“网络功能模块”的线程调度、 数据接收处理、 网络监听、 用户接入及服务、 SNTP时间服务等均作为独立线程编写软件. 其中,主要线程流程如图 6所示,分别完成自然电场观测数据的准实时采集(交换)和处理,网络环境下的多用户并发数据通信,与时间网络服务器准实时同步等操作.
在基于ARM平台的WinCE操作系统下,WEB Server只是部分兼容基于X86平台Windows系统下的IIS服务器系统,也不具备Linux操作系统下的CGI功能所需的环境变量,这为WEB服务网页的编写带来很大的困难. 为此,我们采用一种COM+ASP结构的WEB服务器设计方法,通过远程登录WEB网页实现对仪器状态、 仪器参数、 观测数据、 系统管理、 用户管理等功能进行浏览、 监控和下载.
2.4 环境适应性研究
为了增强全方位自然电场观测系统的环境适应性,满足在地震监测领域的有关使用要求,自然电场观测技术系统的研究过程中,在保证其总体性能和功能设计的情况下,在小型化、 低功耗等便携式应用方面和环境温度适应性方面作了比较多的辅助性研究工作.
1)小型化设计. 经过多次试验和方案优化,在电路设计时,选用了各类大规模集成化的器件和模块,以优化布局,减少几何尺寸. 数据测量模块中,除了保证各项性能指标的关键设计部位之外,基本上均选用了能够实现多通道测量,集成了放大、 模数转换、 数模转换、 数字滤波等功能的混合型模数转换器件,并选用了多接口的SOC主控器件、 高集成度SRAM外围器件以及以表面贴封为主的接口和逻辑器件等; 网络通信与控制模块中,在实现功能试验和程序设计的基础上,定制了由多层板和表面贴封焊接的模块化电路等.
2)低功耗设计. 通过选用低功耗元器件,降低系统工作频率,合理使用休眠模式,优化软硬件设计等途径,基本实现了比较低的系统工作功率损耗,整机功耗可以达到不大于2 W(胡明朝等,2011). 特别是在网络通信与服务功能中采用的ARM技术是一种执行较少类型计算机指令的微处理器,相对于基于复杂指令集计算机(complex instruction set computer,简写为CISC)的X86微处理器而言,这种基于精减指令集计算机(reduced instruction set computer,简写为RISC)的ARM微处理器具有运行效率高、 体系结构简单、 功耗较低等特点,是降低整体功耗的关键技术之一.
3)环境温度适应性设计. 为了提高自然电场观测系统对野外工作环境温度的适应能力,在器件和器材筛选时,全部采用工业级标准,理论上在-45°C—55°C范围内,能够正常工作. 实验室高低温冲击和保持试验显示,在-30°C—40°C温度变化范围内,湿度不低于85%的情况下,能够稳定工作; 在该试验期间,用0.01级饱和标准电池BC9作为标准输入时,自然电场观测技术系统的主机部分对该标准信号的测量记录结果的最大变化误差不大于0.05%.
3. 全方位自然电场观测试验
为了检验自然电场观测技术系统在正常观测条件下的工作状态、 数据产出和网络连接等功能,以及对全方位自然电场随时间动态变化信息的观测和记录,利用研究完成的自然电场观测技术系统试验样机,在天津市静海地震台,开展了全方位自然电场观测试验工作.
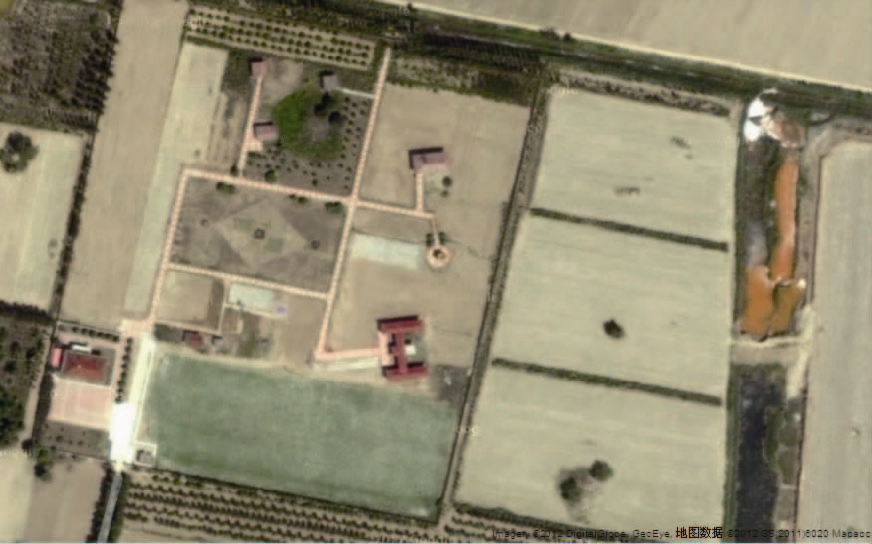
静海地震台的自然电场试验装置系统采用如图 2所示的电极布设方法,开展全方位自然电场观测试验. 观测装置系统在静海地震台的布设平面图如图 7所示,测区一半位于静海地震台的地磁观测区,另一半位于台站东围墙外的农田中,电极埋设深度为3 m. 观测台站周围无较大电磁干扰源; 测区周围有灌溉渠和水塘,水塘在雨季有积水现象.
图 7中,电极P1距离东侧南北走向的池塘约5 m,电极P7距离北部东西走向的引水渠约2 m. 在试验开始阶段(2010年10月),引水渠和池塘基本处于满水位; 在试验观测期间,随着季节的变化,该水位逐步变为干枯状态.
在观测系统连接时,CH0—CH7的所有测道的负极与中心点“P0”电极连接,正极依次与P1—P8电极连接. 在“P0”电极处另埋设两只测试电极,即“P01”和“P02”,测试电极的埋设深度为2 m. 测试电极“P01”,“P02”与“P0”电极一起,两两组合成三组信号输入,与CH9—CH11三个辅助测道连接,用于对装置系统的稳定性进行检测和分析.
静海地震台的自然电场试验观测系统于2011年9月开始工作. 在试验观测期间,利用天津市地震局前兆台网区域网,通过“中国地震前兆台网数据管理系统”对每天的观测数据进行自动或人工汇集,汇集数据进入天津市地震局备用数据库,并可通过“中国地震前兆台网数据处理系统”进行分析、 绘图和预处理.
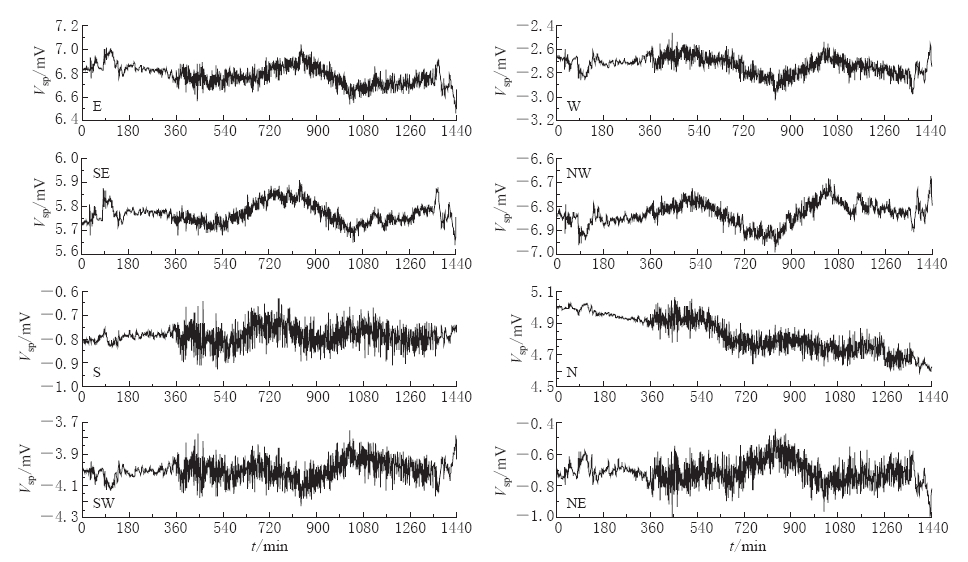
图 8给出2011年10月8日8个主测道的分钟值观测曲线. 从图中可以看出,由于数据吐出率为1次/分钟,观测数据中也记录到了大地电场日变化信息和天津地铁运营干扰信号. 分析这些数据,可见每个测量方向两个测道(NS测向对应N,S测道; EW测向对应E,W测道; NE测向对应NE,SW测道; NW测向对应NW,SE测道(图 8))的观测数据的变化形态具有比较好的一致性,变化方向相反是由于对应测道的正负极连接方式不同所致.
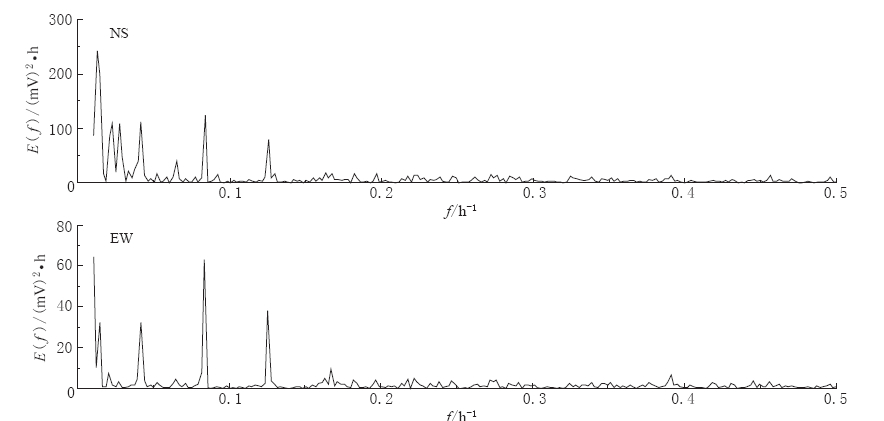
图 9给出NS和EW两个方向的功率谱计算数据曲线. 该数据由2011年10月观测数据的小时均值,利用快速傅里叶变换(fast Fourier transform,简写为FFT)算法计算得到. 由图 9可见,在8 h,12 h和24 h周期点的功率谱变化比较突出. 这种变化符合大地电场的变化特性,由此说明该原始观测数据包含了大地电场的变化成分.
图 10给出3个辅助测道对“P0”,“P01”和“P02”三个埋设在同一点(埋设深度略有差异)的每两个电极之间输出的电压信号的测试结果(该电压信号的主要变化为电极与大地接触过程中产生的极化电位差等). 从图 10中可以看出,在2011年10月1日—11月20日期间,3个辅助测道测量得到的数据变化均比较稳定,11月20日以后的数据变化略有波动,该变化是否与地表环境条件有关尚需进一步考证.
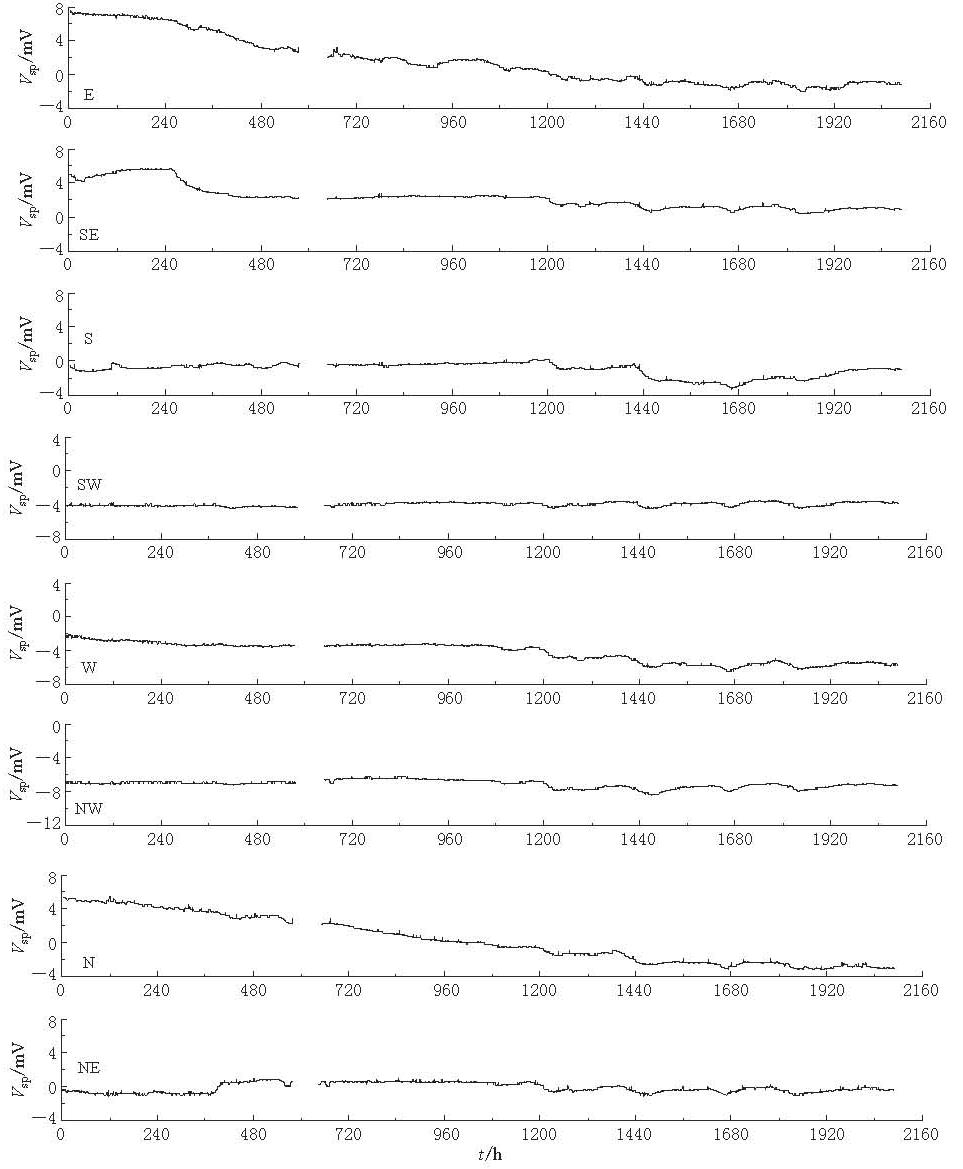
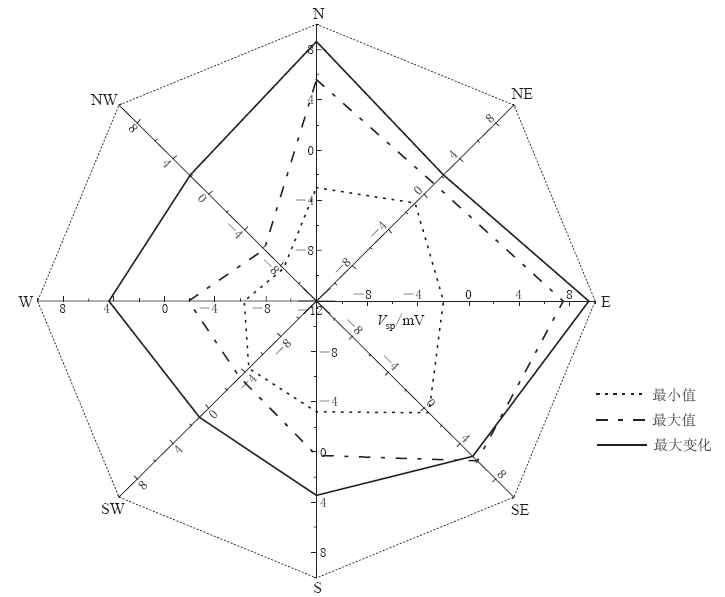
图 11,12分别示出2011年10月1日—12月31日,8个测道的自然电场随时间变化曲线(小时均值),以及全方位自然电场最大变化图谱. 其中大地电场变化成分已经通过1.1节所示的数值处理方法进行了滤除. 图 11中,东向和北向分量变化比较大,主要特征为2011年10月1日—11月20日(0—1200 h),东向(E)分量和北向(N)分量均呈现缓慢下降趋势,最大变化幅度接近10mV,2011年11月20日以后趋于平稳. 根据对台站周边环境的调查和分析,以及对测量电极极化电位变化的初步评估,认为该变化可能与地表水(引水渠、 积水塘附近)的季节性变化有关,该数据缓慢下降时间段正好与地表水由积水期向枯水期的转换过程吻合.
天津市静海地震台的试验观测结果表明,本文研究的全方位自然电场观测技术系统能够获得试验区域自然电场及其随时间的动态变化特点. 截止发稿日期,静海地震台的自然电场观测试验工作仍在继续进行中.
4. 讨论与结论
自然电场是一种物理意义比较明确,变化(孕震)机理相对明晰的地球物理场,在地球物理勘探领域有着比较广泛的应用,在地震监测中也有了多年的探索和实践. 全方位自然电场观测方法是一种类环形梯度法. 该方法能够捕捉到各个方向上的自然电场及其随时间的变化,避免造成自然电场变化信息的遗漏和最大数据变化方位的缺失,在区域性的组网观测时,有望获取可能出现的自然电场随时间和空间变化特征.
以全方位自然电场观测方法为基础的自然电场观测技术系统,能够实现多个测道(最大12个)、 高精度自然电场观测; 配合全方位自然电场观测方法及装置系统布设方法,能够在360°范围内开展自然电场及其随时间变化的动态变化测量,对自然电场指向性测量的空间分辨能力不大于45°; 结合备用测道和辅助通道,能够实现装置系统稳定性的对比观测和自动检验; 能够在现有地震前兆台网中入网观测; 能够实现便携式及野外无人值守观测等.
天津市静海地震台的试验结果表明,该全方位自然电场试验观测系统能够记录到测区及周边自然电场的变化,观测技术系统在试验期间工作状态比较稳定可靠. 其中在2011年10月1日—11月20日期间N向分量和E向分量的趋势性缓慢变化,可能与周边水系的季节性变化有关.
-
-
胡明朝, 席继楼, 刘超, 李晓鹏. 2011. 地电场观测的低功耗技术研究[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 32(1): 71-76. 李金铭(主编). 2005. 地电场与电法勘探[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 36-55. 刘耀伟, 牛安福, 卢军(主编). 2004. 强地震短期前兆异常的物理解释[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 7-14. 莫承彬, 陈忠献. 1995. 自然电场法剧变场的起因初探及其应用[J]. 物探与化探, 19(4): 315-318. 钱复业, 赵玉林. 2005. 地电场短临预报方法研究[J]. 地震, 25(2): 33-40. 钱家栋, 顾左文, 赵家骆, 杨冬梅, 席继楼, 高玉芬, 周锦屏, 毛先进, 郑兆必, 赵国泽, 周勋, 马森林, 陈小斌, 王继军, 马钦忠, 谭大诚, 唐宇雄, 姚同起. 2004. GB/T19531.2-2004地震台站观测环境技术要求(第2部分: 电磁观测)[S]//地震台站观测环境技术要求. 北京: 中国标准化出版社: 14-29. 钱家栋(主编). 2010. 地震电磁学理论基础与观测技术[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 222-239. 宋艳茹, 席继楼, 刘超, 李晓鹏, 庄楠, 徐学恭, 尚先旗, 赵金波. 2011. 一种Pb-PbCl2不极化电极试验研究[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 32(6): 97-103. 谭大诚, 赵家骝, 席继楼, 杜学彬, 徐建明. 2010. 潮汐地电场特征及机理研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(3): 544-555. 谭大诚, 王兰炜, 赵家骝, 席继楼, 刘大鹏, 于华, 陈军营. 2011. 潮汐地电场谐波和各向波形的影响要素[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(7): 1842-1853. 王俊业. 2002. 应用自然电场法研究地下水流场[J]. 工程勘探, (3): 69-71. 席继楼, 赵家骝, 王燕琼. 1999. 大地电场测量系统中的特殊抗干扰技术[J]. 电子技术应用, 54(12): 30-32. 席继楼, 蔡晋安, 赵家骝, 钱家栋, 马钦忠, 卢军, 杜学彬, 谭大诚, 郑兆苾, 毛桐恩, 黄伟, 韩润泉, 叶青, 刘超, 邱颖. 2009. DB/T34-2009地震地电观测方法: 地电场观测[S]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-12. 叶青, 杜学彬, 周克昌, 李宁, 马占虎. 2007. 大地电场变化的频谱特征[J]. 地震学报, 29(4): 382-390. -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 李学波,卫定军,李学涛,罗龙. 与气压有关的地电场特征及机理研究. 地震学报. 2023(01): 62-75 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 刘建波,雷生学,张明东,刘文兵,刘金城,马义山. 用自然电位估算地铁干扰大小——以天津塘沽地震台为例. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2023(05): 107-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. Guoze ZHAO,Xuemin ZHANG,Juntao CAI,Yan ZHAN,Qinzhong MA,Ji TANG,Xuebin DU,Bing HAN,Lifeng WANG,Xiaobin CHEN,Qibin XIAO,Xiangyu SUN,Zeyi DONG,Jijun WANG,Jihong ZHANG,Ye FAN,Tao YE. A review of seismo-electromagnetic research in China. Science China(Earth Sciences). 2022(07): 1229-1246 .  必应学术
必应学术
4. 赵国泽,张学民,蔡军涛,詹艳,马钦忠,汤吉,杜学彬,韩冰,王立凤,陈小斌,肖骑彬,孙翔宇,董泽义,王继军,张继红,范晔,叶涛. 中国地震电磁研究现状和发展趋势. 中国科学:地球科学. 2022(08): 1499-1515 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王宇,谭大诚,邱大琼,张锋,陈亮. 2020年新疆于田M_S6.4地震和田台地电场异常的测道差异性. 地震. 2021(02): 180-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 席继楼. 地电场观测方法与观测技术研究. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2019(02): 1-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 席继楼,庄楠,刘超,颜晓晔,钟李彬,刘华姣. 自然电场全方位观测试验与地表影响因素分析研究. 地震. 2018(04): 49-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 席继楼,关华平,刘超,庄楠,杨晓明,张治国,次卓嘎,格桑卓玛,马爱明. 2015年尼泊尔8.1级地震前后拉萨地电场观测数据变化分析. 地震. 2016(02): 1-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. Xi Jilou,Guan Huaping,Liu Chao,Zhuang Nan,Guan Xinying,Yang Xiaoming,Zhang Zhiguo,Ci Zhuoga,Kelsang Drolma,Ma Aiming. Analysis and Study on the Change of the Observed Geo-electric Field Data at Lhasa Geomagnetic Station before and after the Nepal M_S8. 1 Earthquake. Earthquake Research in China. 2016(04): 526-541 .  必应学术
必应学术
10. 谭大诚,赵家骝,刘小凤,范莹莹,刘君,陈军营. 自然电场的区域性变化特征. 地球物理学报. 2014(05): 1588-1598 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)




 下载:
下载: