Surface wave tomography of Guangdong and its adjacent areas from ambient seismic noise
-
摘要: 通过收集广东及其邻域104个固定地震台站近10个月的垂直分量连续波形数据资料, 使用地震背景噪声互相关格林函数方法, 获得了大部分台站对的背景噪声互相关曲线. 基于这些对称叠加的互相关曲线, 利用时频分析方法, 进一步提取了该地区周期为5—40 s的基阶瑞雷波群速度频散曲线. 其噪声来源分析结果显示: 广东及其邻域的噪声场来源有很强的方向性, 短周期(5—10 s)噪声主要来自东南方向, 范围基本与海岸线分布一致, 可能是由于近海水陆相互作用产生的;较长周期 (15—30 s) 噪声主要来自三大洋的方位. 以这些提取的噪声面波资料为基础, 采用噪声面波层析成像方法反演得到了该地区周期为5—28 s的瑞雷波群速度层析成像图, 从该图可以看出, 广东及其邻域地下结构的横向变化总体较小, 沉积层厚度较薄, 地壳中可能普遍存在一个低速层;从研究区历史地震的分布及其表层地质构造的发育特征来看, 地震主要分布在高、低速过渡带附近, 表明面波群速度与地震之间具有较强的耦合关系;从群速度的低速异常特征来看, 广东及其邻域普遍分布的温泉和高地热主要受深部构造的控制和影响.Abstract: We obtain the ambient noise cross-correlation curves for most of the station-pairs using 10 months of continuous data from the 104 permanent seismic stations of the Guangdong seismic network and its surrounding regions. Based on these symmetrically superimposed cross-correlation curves, we complete Rayleigh wave group velocity dispersion measurements for the periods from 40 s down to about 5 s using time-frequency analysis method. Ambient noise source analyses show that in Guangdong and its neighbor areas, sources of noise field has a strong directionality. Short-period noise (5—10 s) is mainly from the southeast, and its distribution is consistent with the scope of the coastline, so it may be caused by interaction of coastal land and water. Longer-period noise (15—30 s) mainly comes from the orientation of the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Oceans. Furthermore, we obtain the Rayleigh wave group velocity distribution maps in the whole studied area for the periods from 5 s to 28 s using the ambient surface wave tomography algorithm. The tomographic results revealed that in Guangdong and its adjacent areas the crustal lateral variation is small, and the surface sediment thickness is thinner, indicating that there may be a widespread low-velocity layer in the crust. According to the characteristics of history earthquakes and surface geological structure, it can be obtained that earthquakes are mainly distributed in the vicinity of high- and low-velocity transitional zone, suggesting there is a strong coupling relationship between surface wave velocity and earthquakes. From low group velocity anomaly, it is inferred that the high geothermal and hot springs widely distributed in Guangdong and its neighbor areas is mainly under the control and influence of the deep structure.
-
引言
广东及其邻域(18°—28°N,106°—120°E)位于我国东南沿海,地处欧亚大陆东南缘,上新世末—更新世以来,由于印度洋板块、菲律宾海板块与欧亚板块的碰撞、推挤和台湾海峡的近期扩张,导致该区出现较强烈的新构造活动(魏柏林,2001).特别是沿着沿海的滨海断裂带,粤西与广西沿海交界的北部湾地区、珠江口外海地区、粤东与闽西交界的地区,都是重要的中强地震活跃区(陈恩民,黄咏茵,1984;姚伯初等,1994).因此深入研究该区域的地壳速度结构的分布特点,一方面有助于了解该地区地壳结构中蕴含的岩石圈物质流动的地球物理证据,揭示该区断裂活动规律,探讨大陆构造物理及造山运动特征;另一方面对该区域内地震监测预报、工程地震、地震应急等方面的研究具有理论意义和实际应用价值.
利用相邻地震台站记录的背景噪声互相关提取短周期面波的格林函数,并进行层析成像反演是近年来发展迅速的一种新的地震成像方法.数值试验和理论推导都已证明(Lobkis,Weaver,2001; Derode et al,2001,2003;Weaver,2005; Campillo,2006; Gouédard et al,2008),在均匀散射场中,任意两点间的格林函数可以由该两点连续记录的位移的互相关函数中提取出来.Sabra等(2005a)根据同一平面上均匀分布的点源噪声源在半无限三维空间中的传播理论,证明了这样提取的信号与两个台站间的格林函数只存在幅度上的差异.
Shapiro等(2005)通过对美国加州地区USArray台阵的62个地震台站记录到的一个月的地震背景噪声进行互相关,得到了仅与台站间格林函数有幅度差异的互相关函数,并据此提取出了短周期的面波频散曲线;然后通过面波层析成像方法,进一步得到了该地区周期为7.5 s和15 s的瑞雷波群速度分布图像.相比于传统的基于地震面波的层析成像方法,这种新的地震成像方法由于不受震源分布、震源位置误差,以及短周期面波衰减的影响而特别适合于少震地区的区域面波层析成像研究.尤其是该方法可以获得较短周期(如5 s)的频散曲线,因此可以对上地壳有较好的分辨率.近年来该方法在美国、欧洲、澳大利亚东南部、南非、中国等国内外多个区域得到广泛应用(Yao et al,2006; Brenguier et al,2007;Lin et al,2007; Yang et al,2007; Zheng et al,2008,2011; Zhou et al,2012).本文利用广东省“十五”数字地震台网及周边省份的部分台站记录的垂直分量地震背景噪声数据,通过互相关方法提取相邻地震台站短周期面波的经验格林函数,进而采用澳大利亚国立大学Rawlinson(2008)提出的地震面波快速匹配层析成像(fast marching surface tomography package,简写为FMST)方法,得到了周期为5—28 s的瑞雷波群速度分布图像.
1. 数据和处理方法
本文所用数据为2009年8月—2010年5月记录时间长度为10个月的连续波形的垂直分量. 所用广东及其邻域数据的台站数目为: 广东52、福建10、台湾7、香港7、海南5、广西11、湖南4、江西8,共104个台站.其中14个为短周期台站,其余的为60 s或120 s的宽频带台站,还有一个台站(GZH)为360 s的甚宽频带台站.台站分布如图1所示.
![]() 图 1 用于噪声互相关提取的台站分布图细黑线为省界,粗黑线为断层分布(邓起东,2007),白色粗虚线为从CHZ台到SCD台的大圆路径
图 1 用于噪声互相关提取的台站分布图细黑线为省界,粗黑线为断层分布(邓起东,2007),白色粗虚线为从CHZ台到SCD台的大圆路径房立华(2009)、Bensen等(2007)和Rawlinson(2008)对利用地震噪声提取频散曲线和面波层析成像的方法和技术等进行了详细的介绍,因此下面仅对本研究中的数据处理流程和方法进行简要的描述.
首先,通过地震背景噪声互相关方法得到台站间的经验格林函数.为了减少台站仪器差异、地震信号、台站附近干扰源等因素对噪声互相关的影响,减少互相关的计算时间,需要对连续背景噪声数据进行去仪器响应、滤波、重采样以及时域归一化等数据预处理.目前主要使用的时域归一化方法有“one-bit”(Larose et al,2004)方法、剪切阈值法(Sabra et al,2005b,c)、地震事件自动检测和移除法、滑动绝对平均归一化(running absolute mean normalization)方法和水准量迭代归一化(iterative water-level normalization)方法(Bensen et al,2007).Bensen等(2007)对上述几种时域归一化方法进行了对比研究.根据其研究结果,我们选择了滑动绝对平均归一化方法对本文的连续波形数据进行时域归一化预处理.该方法通过选取一个固定长度的归一化滑动时间窗,计算出该时间窗内连续波形的绝对值的均值,以该均值的倒数为归一化权重,对位于滑动窗中心处的连续波形值进行加权.数据预处理后,我们按"日"对10个月的数据进行互相关计算和叠加.为了减小噪声源分布不均的影响和进一步提高信噪比,通过对叠加后的互相关曲线的因果支和非因果支进行反向叠加,最终得到台站间的经验格林函数. 然后,当得到的台站间经验格林函数的信噪比足够高时,通过采用时频分析方法(Levshin et al,1992)即可测量得到台站间的瑞雷波群速度频散曲线.我们利用Rawlinson(2008)提出的FMST方法,对台站间测量得到的群速度频散进行反演,最终得到研究区域的瑞雷波群速度图.该层析成像方法通过对波动方程进行差分计算,利用最小走时原理快速计算出台站间的射线在二维球面上的理论走时,并利用观测走时与理论走时之差值,采用子空间反演方法,得到反演模型节点上的速度校正值.
2. 结果
根据前面所述方法,从10个月的连续背景噪声互相关曲线中,对大部分台间距大于120 km的台站对,我们都能获得清楚的瑞雷波信号.图2是典型的背景噪声经验格林函数、噪声源来源方位以及瑞雷波群速度频散曲线的测量图.互相关曲线图(图2a,b)显示,在不同震中距和不同频带下,互相关曲线的峰值都非常明显,这表明在整个研究区域内,经验格林函数都能够清晰地获取到.图2b中,互相关曲线对称峰值的幅值差异表明背景噪声源强度分布的非均匀性.为了进一步研究噪声源的方位及来源,首先对互相关曲线按噪声源频段分布进行带通滤波,然后对滤波后的互相关曲线进行归一化,最后根据每对台站的方位角及其归一化后的因果支和非因果支的最大值,得到图2c给出的4个频段的噪声来源方位分布图.从图2c中可以看出,5—10 s周期段的高频噪声来源的方向性非常明显,主要来源于东南方向(方位大致为45°—120°),散布范围大致与研究区域的海岸线平行,因此推测噪声的来源主要是由于浅海的水陆相互作用引起的.这一结果与Stehly等(2006)利用南加州地震台阵获得的观测结果类似.特别是在台湾海峡方位,噪声的不均匀性特别明显,可能是海峡间水陆作用更为剧烈所致.随着频段的周期变大,噪声来源的方向性相对减小.其中10—15 s周期段的噪声来源的方位主要变为东南(太平洋)、西南(印度洋)和北偏西(大西洋).其中东南方向的噪声源较强,其方位与中国台湾岛和菲律宾之间的巴士海峡的方位一致,说明岛屿与岛链对远洋噪声具有一定的阻挡作用.
![]() 图 2 瑞雷波经验格林函数、噪声强度方位分布及噪声互相关频散曲线测量图 (a)MEZ台与其它台站之间的噪声互相关曲线;(b)CHZ-SCD台站对之间的经验格林函数在不同周期段的带通滤波;(c)不同周期段的噪声源方位分布;(d)CHZ-SCD台站对之间的瑞雷波群速度频散曲线的测量.白色实线表示实测群速度值,黑色虚线表示基于华南地壳速度结构模型(郑圻森等,2003)的理论群速度值Figure 2. Example of Rayleigh wave empirical Green’s function,orientation distribution of noise intensity and dispersion measurements obtained from ambient seismic noise correlations (a)Ambient noise correlations between the station MEZ and other stations;(b)Empirical Green’s function filtered in different frequency b and s for the CHZ-SCD path;(c)Orientation distribution of noise intensities in different frequency b and s;(d)Rayleigh wave group velocity dispersion curve for the CHZ-SCD path.The white solid line represents the measured value,the black dashed curve is the theoretical value from the South China crustal velocity model(Zheng et al,2003)
图 2 瑞雷波经验格林函数、噪声强度方位分布及噪声互相关频散曲线测量图 (a)MEZ台与其它台站之间的噪声互相关曲线;(b)CHZ-SCD台站对之间的经验格林函数在不同周期段的带通滤波;(c)不同周期段的噪声源方位分布;(d)CHZ-SCD台站对之间的瑞雷波群速度频散曲线的测量.白色实线表示实测群速度值,黑色虚线表示基于华南地壳速度结构模型(郑圻森等,2003)的理论群速度值Figure 2. Example of Rayleigh wave empirical Green’s function,orientation distribution of noise intensity and dispersion measurements obtained from ambient seismic noise correlations (a)Ambient noise correlations between the station MEZ and other stations;(b)Empirical Green’s function filtered in different frequency b and s for the CHZ-SCD path;(c)Orientation distribution of noise intensities in different frequency b and s;(d)Rayleigh wave group velocity dispersion curve for the CHZ-SCD path.The white solid line represents the measured value,the black dashed curve is the theoretical value from the South China crustal velocity model(Zheng et al,2003)从图2b同一台站对的不同周期段的经验格林函数图中,可以直观地看到频散现象.根据台站对间的经验格林函数,从瑞雷波信噪比大于12的台站对间 测量得到了该台站对间的基阶瑞雷波群速度频散曲线(图2d).从图2d可以看出,在短周期(10 s以内)部分,实测的群速度值低于理论群速度值;在长周期部分,实测的群速度值比理论值要偏大.短周期部分群速度值偏低可能是由于沿海地区地表存在一定厚度的沉积层引起的,而长周期部分的群速度值偏高则是由于沿海地区的地壳厚度相对于华南地区的平均地壳厚度要薄(郑圻森等,2003;沈玉松等,2013)引起的.
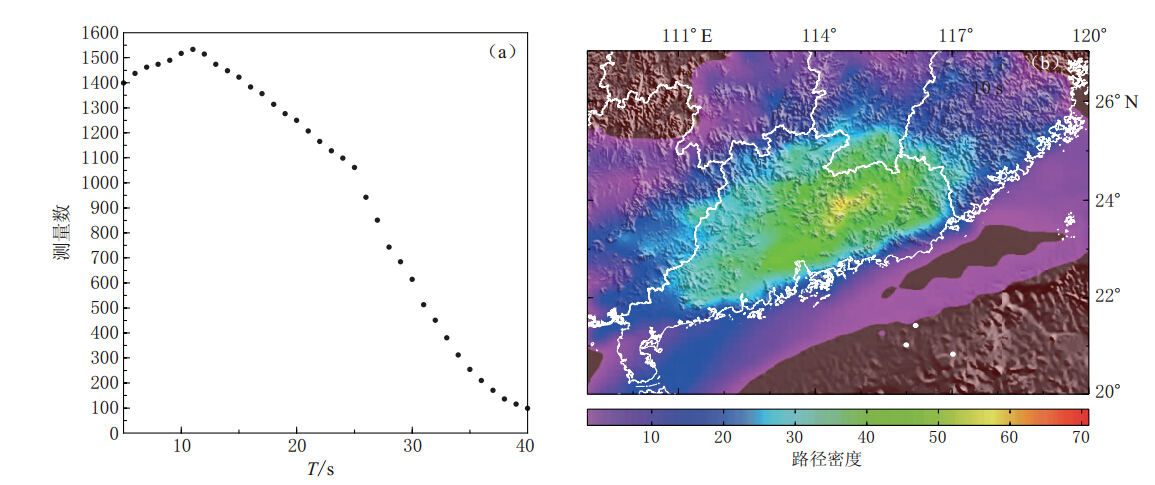
从所有信噪比大于12的经验格林函数中,我们测量得到的频散曲线的周期范围为5—40 s(图3a).从图3a可以看出,具有较好测量路径数的周期范围为5—28 s.在该周期范围内的每个周期点上,测量路径数都大于600,测量路径基本上覆盖了整个广东及其周边地区(图3b).特别是在粤东地区,由于台站分布更为均匀和密集,射线的覆盖率比其它地区更高.
![]() 图 3 不同周期测量得到的频散路径数分布(a)和0.25°×0.25°网格条件下周期为10 s时的频散路径密度分布(b).在周期为5—28 s范围内,频散路径的密度分布在空间上类似Figure 3. (a)Distribution of the number of dispersion paths for different periods;(b)Ray density map for the period of 10 s,the ray density is the number of rays passing through a 0.25 degree by 0.25 degree cell.In the period range of 5—28 s the ray coverage is similar in space
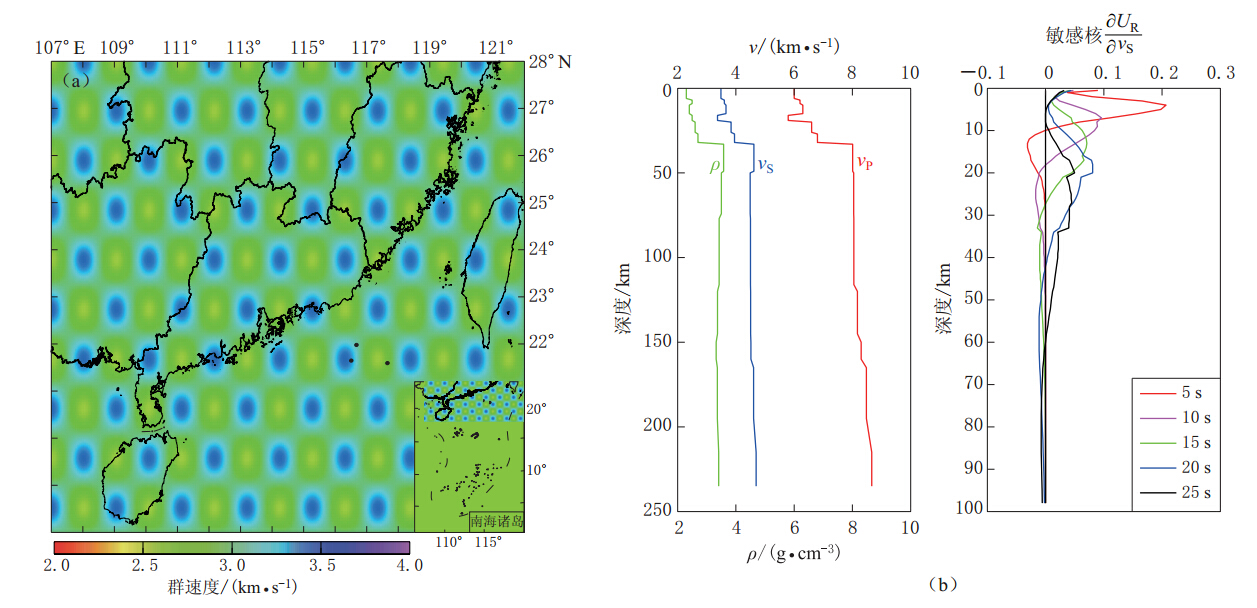
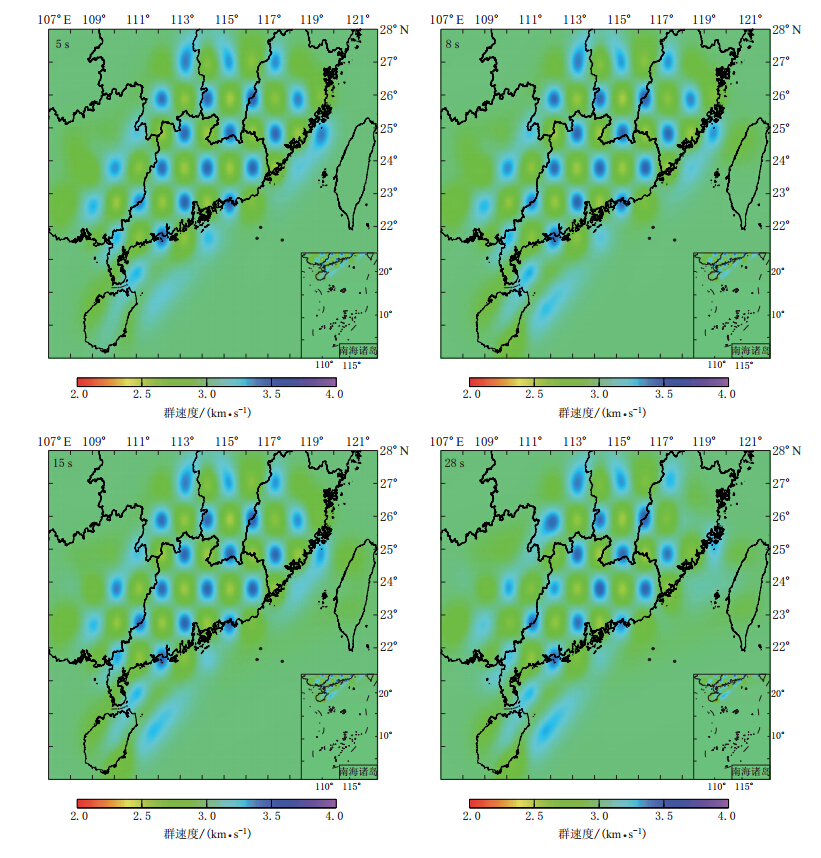
图 3 不同周期测量得到的频散路径数分布(a)和0.25°×0.25°网格条件下周期为10 s时的频散路径密度分布(b).在周期为5—28 s范围内,频散路径的密度分布在空间上类似Figure 3. (a)Distribution of the number of dispersion paths for different periods;(b)Ray density map for the period of 10 s,the ray density is the number of rays passing through a 0.25 degree by 0.25 degree cell.In the period range of 5—28 s the ray coverage is similar in space为了检验各周期的射线路径分布的反演分辨率,我们对反演区域进行了1°×1°分辨率 的检测板实验.图4a为反演区域内1°×1°分辨率的检测板,检测板的速度扰动幅度为 ±0.4 km/s.图4b为不同周期的群速度对地下速度结构的敏感深度图,随着频散周期的增加,研究区域的群速度分布受地表浅层地质构造的影响逐渐减小.图5给出了周期为5,8,15,28 s的检测板实验层析成像反演结果.从图5可以看出,在北东—南西方向的广东及其周边区域内,检测板中速度扰动的幅度和形状都能较好地反演出来,而在反演区域的西北部和东南部,由于射线路径的缺失,检测板中的速度扰动基本不能反演.因此本文中只讨论北东—南西方向的广东及其邻域的 层析成像结果.根据不同周期的测量路径数和射线覆盖密度,我们反演得到了广东及其周边地区周期为5—28 s的瑞雷波群速度分布图(图6).从图6中5 s的短周期群速度图可以看出,该地区的群速度呈高低交替变化状态,对应地形相对较高的山脉地区的群速度相对较大,而在山脉与山脉之间的过渡区域群速度相对较小.这与研究区域中沉积层、岩浆岩、变质岩交替出现的复杂地表地质构造(魏柏林,2001)现象比较一致.在粤北的南雄、梅州以及粤东沿海的南澳一带,5 s的群速度分布图上存在一些低速区,这可能与该地区的地质构造中存在着一些较新的沉积层有关.从图6中周期为5 s和8 s的群速度分布图的变化可以看出,随着频散周期的增加,群速度总体上增大,群速度图的横向变化逐渐减小.说明广东及其邻域的地壳浅层地质构造比较复杂,随着深度的增大,地壳结构的横向变化逐渐显示出均一化 的趋势.但从反演得 到的周期为15 s的群速度图上可以看出,相对于5 s和8 s的群速度图,该周期的群速度总体上变小了,结合图4b中周期为15 s对应的敏感深度,可以推测在广东及其邻域的地壳中存在一个低速层.
另外,从图6周期为5 s和8 s的群速度分布图上的地震(小黑点)分布情况来看,地震主要分布在群速度的高低速过渡区.而根据田有等(2007)的研究表明,高速区域一般是脆性的岩壳层,比较容易集中应力,而低速区域则可能代表了破碎程度高、富含流体或温度较高的区域.低速体易于传递能量,但难以积累能量;而高速体则容易积累引发地震的应变能.高低速异常体的过渡带既是应力集中的地方,又是介质相对比较脆弱的地方,这样的环境具备了积累大量应变能的介质条件,容易发生破裂,释放应力,因而容易引发地震.所以,周期为5 s和8 s的群速度分布图上的地震分布特征也在一定程度上表明了地壳结构的不均匀性,而且地壳的不均匀性也主要表现在浅层的上地壳,这与该地区的一些地震精定位研究所得到的地震深度相一致(康英等,2007;叶秀薇等,2009).
广东及其邻域的地壳厚度总体上比较平坦,平均厚度在29 km左右,由西北向东南地壳厚度逐渐变薄,总体厚度变化在6 km左右(尹周勋等,1999;郑圻森等,2003;Zhang,Wang,2007;黄晖等,2010;沈玉松等,2013),所以周期为28 s群速度分布图像中的低速群速度异常区不太可能是由于地壳厚度的变化引起的.根据熊绍柏等(1991)的研究显示,广东及周边福建地区具有广泛的温泉和地热分布,这些地热可能是地幔的热源通过一些断裂通道向地壳内运移形成的,这可能是引起周期为28 s群速度分布图像中出现低速异常的可能原因.
3. 讨论与结论
广东及其邻域毗邻南海北部陆缘,来自海洋的背景噪声极其丰富,是研究噪声特性并利用噪声进行结构研究的极佳场所.通过对广东及其邻域内数字地震台的10个月连续波形记录的互相关,发现研究区域内的噪声来源具有较强的非均匀性,尤其是短周期噪声(5—10 s)的非均匀性特别明显,主要来自东南沿海方向,基本与东南沿海的海岸线分布相 一致,这说明该周期段的噪声可能是由于近海的水陆相互作用引起的;而长周期(15—20 s,20—30 s)的噪声特性表明其与近海环境之间无很强的相关性,可能主要来自于远洋背景噪声的作用,且获取的噪声来源方位上也基本与三大洋所在方位一致.另外长周期噪声来源的强度显示,岛屿与岛链对远洋噪声可能具有一定的阻挡作用.这些噪声周期来源的差异性也反映了噪声在传播过程中的衰减特性,即短周期噪声主要来源于短距离传播源,而长周期噪声则经历了较长的传播路径.从我们获得的研究区内的瑞雷波经验格林函数,进一步发现了研究区的噪声面波主要集中在周期为5—40 s的群速度频散曲线.通过最终的分析对比,最终使用了周期为5—28 s的面波群速度进行层析成像反演,这主要是由于该周期段的面波不仅来源丰富,而且可靠性很好.从噪声面波层析成像的结果来看,短周期的群速度图像的横向交替变化明显,随着周期增大,群速度图的横向变化逐渐减小.这可能反映了研究区域地壳浅部沉积岩、岩浆岩、变质岩交替出现的复杂的地质构造现象.但整个地壳的S波速度结构横向相对比较均匀,而15 s负频散群速度图像的出现,表明广东及其邻域的地壳中可能普遍存在一个低速层.另外短周期的群速度分布与研究区域内的历史地震分布具有较大的关联性,而较长周期(28 s)的群速度分布可能揭示了研究区域内广泛分布的温泉和地热的成因.
当然,由于在粤北及其周边的湖南、江西以及南海海域地区台站稀少,导致层析成像结果在粤北和沿海边界区域的分辨率不够高.随着区域永久地震台站(特别是海岛台站)的增加,我们将在下一步的研究中增加新的台站数据资料,提高频散曲线的提取频率,以便进一步提高对地壳浅层构造的分辨率.
-
图 1 用于噪声互相关提取的台站分布图细黑线为省界,粗黑线为断层分布(邓起东,2007),白色粗虚线为从CHZ台到SCD台的大圆路径
Figure 1. Distribution of seismic stations used for ambient noise correlation Thin dark lines denote provincial boundaries,thick dark lines denote faults(Deng,2007),the thick white dashed line from the station CHZ to SCD indicates the selected great circle path for Fig.2
图 2 瑞雷波经验格林函数、噪声强度方位分布及噪声互相关频散曲线测量图 (a)MEZ台与其它台站之间的噪声互相关曲线;(b)CHZ-SCD台站对之间的经验格林函数在不同周期段的带通滤波;(c)不同周期段的噪声源方位分布;(d)CHZ-SCD台站对之间的瑞雷波群速度频散曲线的测量.白色实线表示实测群速度值,黑色虚线表示基于华南地壳速度结构模型(郑圻森等,2003)的理论群速度值
Figure 2. Example of Rayleigh wave empirical Green’s function,orientation distribution of noise intensity and dispersion measurements obtained from ambient seismic noise correlations (a)Ambient noise correlations between the station MEZ and other stations;(b)Empirical Green’s function filtered in different frequency b and s for the CHZ-SCD path;(c)Orientation distribution of noise intensities in different frequency b and s;(d)Rayleigh wave group velocity dispersion curve for the CHZ-SCD path.The white solid line represents the measured value,the black dashed curve is the theoretical value from the South China crustal velocity model(Zheng et al,2003)
图 3 不同周期测量得到的频散路径数分布(a)和0.25°×0.25°网格条件下周期为10 s时的频散路径密度分布(b).在周期为5—28 s范围内,频散路径的密度分布在空间上类似
Figure 3. (a)Distribution of the number of dispersion paths for different periods;(b)Ray density map for the period of 10 s,the ray density is the number of rays passing through a 0.25 degree by 0.25 degree cell.In the period range of 5—28 s the ray coverage is similar in space
-
陈恩民, 黄咏茵. 1984. 华南十九次强震暨南海北部陆缘地震带概述[J]. 华南地震,4 (1): 11-32. Chen E M, Huang Y Y. 1984. Overview on seismic belt along the northern South China Sea continental margin with the nineteen strong earthquakes in South China[J]. South China Journal of Seismology,4 (1): 11-32 (in Chinese).
邓起东. 2007. 中国活动构造图[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-2. Deng Q D. 2007. Map of Active Tectonics in China[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 1-2 (in Chinese).
房立华. 2009. 华北地区瑞利面波噪声层析成像研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所: 41-73. Fang L H. 2009. Rayleigh Wave Tomography in North-China from Ambient Seismic Noise[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration: 41-73 (in Chinese).
黄晖, 米宁, 徐鸣洁, 王良书, 李华, 于大勇. 2010. 福建地区地壳上地幔S波速度结构与泊松比[J]. 高校地质学报,16 (4): 465-474. Huang H, Mi N, Xu M J, Wang L S, Li H, Yu D Y. 2010. S-wave velocity structures of the crust and uppermost mantle, and Poisson's ratios in Fujian Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,16(4): 465-474 (in Chinese).
康英, 杨选, 黄文辉, 陈杏, 陈贵美, 林伟, 吴华灯. 2007. 阳江地区地震双差定位及其活动图像分析[J]. 中国地震,23 (3): 295-302. Kang Y, Yang X, Huang W H, Chen X, Chen G M, Lin W, Wu H D. 2007. Analysis on high-resolution hypocenter location and activity image of Yangjiang earthquake sequences[J]. Earthquake Research in China,23(3): 295-302 (in Chinese).
沈玉松, 康英, 徐果明. 2013. 广东及其邻域的地壳厚度和泊松比分布[J]. 中国地震,29 (2): 210-218. Shen Y S, Kang Y, Xu G M. 2013. The crustal thickness and Poisson's ratio distribution in Guangdong and its adjacent areas[J]. Earthquake Research in China,29(2): 210-218 (in Chinese).
田有, 赵大鹏, 孙若昧, 滕吉文. 2007. 1992年美国加州兰德斯地震: 地壳结构不均匀性对地震发生的影响[J]. 地球物理学报,50 (5): 1488-1496. Tian Y, Zhao D P, Sun R M, Teng J W. 2007. The 1992 Landers earthquake: Effect of crustal heterogeneity on earthquake generation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,50 (5): 1488-1496 (in Chinese).
魏柏林. 2001. 东南沿海地震活动特征[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-58. Wei B L. 2001. The Characteristics of Seismicity in Southeast Coastal Region[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 1-58 (in Chinese).
熊绍柏, 金东敏, 孙克忠, 邹以生, 樊叙邦, 杜小刚. 1991.福建漳州地热田及其邻近地区的地壳深部构造特征[J]. 地球物理学报,34 (1): 55-63. Xiong S B, Jin D M, Sun K Z, Zou Y S, Fan X B, Du X G. 1991. Some characteristics of deep structure of the Zhangzhou geothermal field and it's neighbourhood in the Fujian province[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica,34 (1): 55-63 (in Chinese).
姚伯初, 曾维军, 陈艺中, 张锡林. 1994. 南海北部陆缘东部的地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报,37 (1): 27-35. Yao B C, Zeng W J, Chen Y Z, Zhang X L. 1994. The crustal structure in the eastern part of the northern margin of the South China sea[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica,37(1): 27-35 (in Chinese).
叶秀薇, 刘锦, 胡秀敏. 2009. 广东阳江地震序列双差法重新定位结果分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,29 (6): 60-63. Ye X W, Liu J, Hu X M. 2009. Relocation of Yangjiang earthquake sequences with double-difference location algorithm[J]. Joural of Geodesy and Geodynamics,29 (6): 60-63 (in Chinese).
尹周勋, 赖明惠, 熊绍柏, 刘宏兵, 滕吉文, 孔祥儒. 1999. 华南连县-博罗-港口地带地壳结构及速度分布的爆炸地震探测结果[J]. 地球物理学报,42 (3): 383-392. Yin Z X, Lai M H, Xiong S B, Liu H B, Teng J W, Kong X R. 1999. Crustal structure and velocity distribution from deep seismic sounding along the profile of Lianxian-Boluo-Gangkou in South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophy-sics,42 (3): 383-392 (in Chinese).
郑圻森, 朱介寿, 宣瑞卿, 蔡学林. 2003. 华南地区地壳速度结构分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,23 (4): 9-13. Zheng Q S, Zhu J S, Xuan R Q, Cai X L. 2003. An approach to the crustal velocities in Southern China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,23(4): 9-13 (in Chinese).
Bensen G D, Ritzwoller M H, Barmin M P, Levshin A L, Lin F, Moschetti M P, Shapiro N M, Yang Y. 2007. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements[J]. Geophys J Int,169 (3): 1239-1260.
Brenguier F, Shapiro N M, Campillo M, Nercessian A, Ferrazzini V. 2007. 3-D surface wave tomography of the Piton de la Fournaise volcano using seismic noise correlations [J]. Geophys Res Lett,34 (2): L02305. doi:10.1029/2006GL028586.
Campillo M. 2006. Phase and correlation in 'Random' seismic fields and the reconstruction of the Green function[J]. Pure Appl Geophys,163 (2/3): 475-502.
Derode A, Tourin A, Fink M. 2001. Random multiple scattering of ultrasound:Ⅱ. Is time reversal a self averaging process? [J]. Phys Rev E,64 (3): 36606-36618.
Derode A, Larose E, Tanter M, Rosny J, Tourin1 A, Campillo M, Fink M. 2003. Recovering the Green's function from field-field correlations in an open scattering medium[J]. J Acoust Soc Am,113 (6): 2973-2976.
Gouédard P, Stehly L, Brenguier F, Campillo M, Colin de Verdière Y, Larose E, Margerin L, Roux1 P, Sánchez-Sesma F J, Shapiro N M, Weaver R L. 2008. Cross-correlation of random fields: Mathematical approach and applications[J]. Geophys Pros,56 (3): 375-393.
Larose E, Derode S, Campillo M, Fink M. 2004. Imaging from one-bit correlations of wideband diffuse wave fields[J]. J Appl Phys,95 (12): 8393-8399.
Levshin A, Ratnikova L, Berger J. 1992. Peculiarities of surface-wave propagation across central Eurasia[J]. Bull Seismol Soc Am,82 (3): 2464-2493.
Lin F C, Ritzwoller M H, Townend J, Bannister S, Savage M K. 2007. Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography of New Zealand[J]. Geophys J Int,170 (2): 649-666.
Lobkis O I, Weaver R L. 2001. On the emergence of the Green's function in the correlations of a diffuse field[J].. J Acoust Soc Am, 110 (6): 3011-3017
Lobkis O I, Weaver R L. 2001. On the emergence of the Green's function in the correlations of a diffuse field[J]. J Acoust Soc Am,110 (6): 3011-3017.
Rawlinson N. 2008. FMST: A Spherical Shell (Surface Wave) Tomography Code for Mapping Traveltime Residuals as 2-D Variations in Wavespeed. Version 1.1[CP]. Australian: Australian National University.
Sabra K G, Roux P, Kuperman W A. 2005a. Arrival time structure of the time-averaged ambient noise cross-correlation function in an oceanic waveguide[J]. J Acoust Soc Am,117 (1): 164-174.
Sabra K G, Gerstoft P, Roux P, Kuperman W A, Fehler M C. 2005b. Surface wave tomography from microseisms in Southern California[J]. Geophys Res Lett,32 (14): L14311. doi:10.1029/2005GL023155.
Sabra K G, Gerstoft P, Roux P, Kuperman W A, Fehler M C. 2005c. Extracting time-domain Green's function estimates from ambient seismic noise[J]. Geophys Res Lett,32 (3): L03310. doi:10.1029/2004GL021862.
Shapiro N, Campillo M, Stehly L, Ritzwoller M H. 2005. High-resolution surface-wave tomography from ambient seismic noise[J]. Science,307 (5715): 1615-1618.
Stehly L, Campillo M, Shapiro N M. 2006. A study of the seismic noise from its long range correlation properties[J]. J Geophys Res,111 (B10): B10306. doi:10.1029/2005JB004237.
Weaver R L. 2005. Information from seismic noise[J]. Science,307 (5715): 1568-1569. doi:10.1126/science.1109834.
Yang Y J, Ritzwoller M H, Levshin A L, Shapiro N M. 2007. Ambient noise Rayleigh wave tomography across Europe[J]. Geophys J Int,168 (1): 259-274.
Yao H J, van der Hilst R D, de Hoop M V. 2006. Surface-wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis: Ⅰ. Phase velocity maps[J]. Geophys J Int,166 (2): 732-744.
Zhang Z J, Wang Y H. 2007. Crustal structure and contact relationship revealed from deep seismic sounding data in South China[J]. Phys Earth Planet Inter,165 (1/2): 114-126.
Zheng S H, Sun X L, Song X D, Yang Y J, Ritzwoller M H. 2008. Surface wave tomography of China from ambient seismic noise[J]. Geochem Geophys Geosyst,9 (5): Q0502. doi:10.1029/2008GC001981.
Zheng Y, Shen W, Zhou L, Yang Y, Xie Z, Ritzwoller M H. 2011. Crust and uppermost mantle beneath the North China Craton, northeastern China, and the Sea of Japan from ambient noise tomography[J]. J Geophys Res,116 (B12): B12312. doi:10.1029/2011JB008637.
Zhou L Q, Xie J Y, Shen W S, Zheng Y, Yang Y J, Shi H X, Ritzwoller M H. 2012. The structure of the crust and uppermost mantle beneath South China from ambient noise and earthquake tomography[J]. Geophys J Int,189 (3): 1565-1583.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 戴靠山,汪士权,刘康,游庆瑜. 倾斜边坡多道面波分析中的最小偏移距估计方法. 地震学报. 2022(02): 327-338 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 魏红梅,陈丽娟,王同军. 重庆地区背景噪声面波群速度层析成像. 华南地震. 2020(01): 46-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载: