On the correlation of ground motion parameters with slope stability incorporating topographic effects
-
摘要: 地形对地震动的影响比较复杂, 考虑地形放大效应的地震滑坡稳定性分析需要选择合适的地震动参数. 本文使用自贡地形影响台阵记录到的2008年汶川MS8.0地震主震加速度记录, 分析了地震动峰值加速度、 阿里亚斯烈度以及90%能量持时随地形高度的变化, 探讨了地形效应作用下峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度与地震动作用下斜坡稳定性的相关性. 结果表明: ① 地形场地对峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度均有显著的放大效应. 地形放大效应较为复杂, 其整体上随台站高度的增加而增大, 水平向的放大效应大于竖直向. 水平向峰值加速度的放大系数为1.1—1.8, 阿里亚斯烈度的放大系数为1.2—3.3; 竖直向相应放大系数分别为1.1—1.3和1.2—1.7. ② 地形对地震动持时也有一定的放大效应, 但不同高度、 不同分量的放大效应没有显著差异, 其放大系数均约为1.3. ③ 阿里亚斯烈度和峰值加速度均能很好地表征地形对地震动的影响, 与地震动对斜坡稳定性的影响具有很强的相关性. 与峰值加速度相比, 阿里亚斯烈度综合了地震动的多方面特征, 可以更好地表征地形对地震动的影响, 与地震动作用下斜坡稳定性的相关性更强.Abstract: Topography has complex effects on ground motions. In assessing seismic landslide stability, the proper ground motion parameters are needed considering the topographic effects on slope stability. Based on the strong ground motion accelerations of the main shock of Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake recorded by the Zigong topographic array, we analyzed the variation of peak ground acceleration (PGA), Arias intensity and 95% significant duration against the terrain’s height, and discussed the correlation betweem the stability of slope during an earthquake and PAG/Arias intensity, with the topographic effect being taken into consideration. The following results are concluded. ① The amplification effect of topography on PGA and Arias intensity are both obvious. The amplification effect becomes generally stronger with the height of the terrain increasing, and the amplification effect is more obvious on horizontal ground motions than on the vertical component. For the horizontal ground motions, the amplification factors are between 1.1 and 1.8 for PGAs and between 1.2 and 3.3 for Arias intensity; the amplification coefficient are in the range from 1.1 to 1.3 and 1.2 to 1.7 for the vertical PGAs and Arias intensity, respectively. The discrepant amplification effect on PAG and Arias intensity shows the influence of topographic effects on strong motion is quite complex. ② The topography can also amplify the duration of strong ground motions, but there is slight difference in the amplification effect among records from different heights and for different components, with the amplification factors all being about 1.3. ③ Both Arias intensity and PGA can reflect the effects of topography on ground motions, and have strong correlations with the stability of slope. Compared with PGA, Arias intensity contains more information of the ground motions, and has a better capacity to capture the effects of topography on ground motions and on the potential seismic landslides hazard.
-
引言
震害调查表明,局部地形对震害分布具有重要影响.在1976年唐山大地震中,位于迁西县景忠山顶部的庙宇式建筑被严重破坏,烈度达Ⅸ度,而与其高度相差约300 m的山脚周围村庄的破坏程度则明显较轻,烈度仅为Ⅵ度(杨宇等,2011).2008年汶川MS8.0地震诱发了数以万计的滑坡(吴树仁等,2009),其所在的龙门山地区地形地貌比较复杂,地形高差悬殊,这种复杂的地形对地震动的影响是地震滑坡多发的一个重要原因(罗永红,王运生,2013).与风暴形成的降雨型滑坡沿山体均匀分布不同,地震滑坡多分布在脊峰及山顶部位,具有明显的地形分布特征(Meunier et al,2008).强震观测和数值模拟研究进一步表明,不规则地形对地震动的幅值、 频谱等特性具有显著的影响(刘晶波,1996;Bouckovalas,2005;姜慧等,2007;Lee et al,2009;丁志华等,2014),这是地形影响震害分布的根本原因.
地震动是影响地震作用下斜坡稳定性的重要因素(王秀英等, 2011,2012),地形对地震动的影响也会影响斜坡的稳定性(Peng et al,2009).实际工作中,由于台站分布稀疏不一,往往无法获取不同位置的地震动记录而采用地震动参数表示地震动强度,其中峰值加速度和阿里亚斯(Arias)烈度为两个较为常用的地震动参数(Jibson,2007;王秀英等,2012;徐光兴等,2012).山区具有复杂的地形地貌,地形对地震动的持时、 振幅和频率等特性均会产生显著影响且作用较为复杂(刘洪兵,朱晞,1999;石玉成等,1999;卢育霞等,2011;郭明珠等,2013),而地震动峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度均不能完全涵盖地震动持时、 振幅和频率等特性,因此考虑地形效应影响的地震动作用下的斜坡稳定性,需要选取与斜坡稳定性相关性较好的地震动参数.在评估地震滑坡稳定性的方法中,Newmark(1965)提出的累积位移模型,在斜坡稳定性评价中取得了较好的效果(Jibson,1993;Jibson et al,2000;陈晓利等,2013;葛华等,2013;王涛等,2013).该方法将滑坡体视为在斜坡上滑动的刚滑块,该滑块具有临界加速度,当地震动加速度记录值大于斜坡临界加速度时,滑块产生位移,该位移值的大小则反映了地震动作用下斜坡的稳定性(Jibson,2007).
本文采用Newmark(1965)滑坡稳定评价模型,利用自贡地形影响台阵获取的汶川地震主震加速度记录,分析地形对地震动峰值加速度、 阿里亚斯烈度以及90%地震动能量持时的影响,以期对比在地形效应影响下地震动峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度与地震作用下斜坡稳定性的相关性.
1. 数据
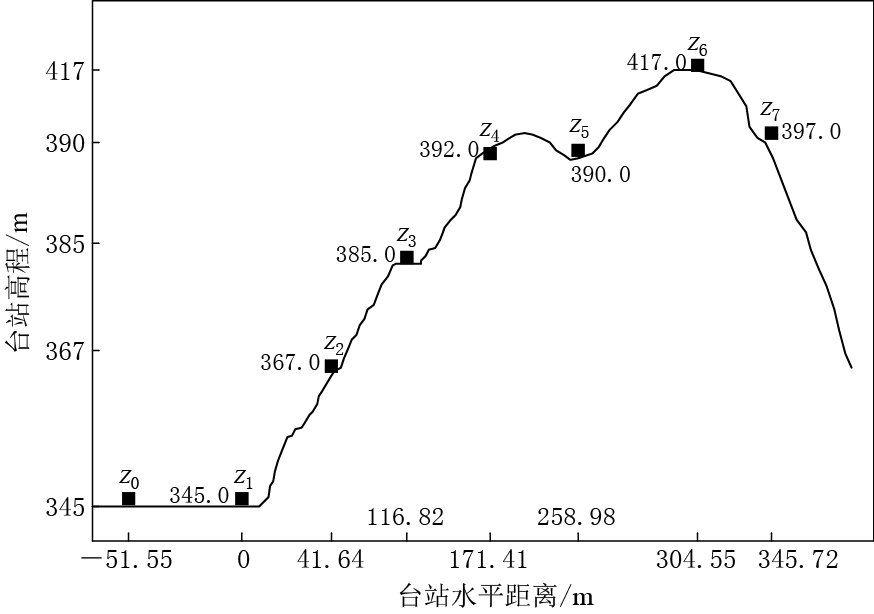
自贡地形影响台阵位于四川省自贡市西山公园.该公园地处自流井凹陷区,总体构造形态为一个复式向斜,由一系列北东向背斜和向斜组成.该台阵场址位于自流井背斜附近,基本沿着山脊地形的轴线,观测对象为山脊地形.该台阵由8个台站(Z0,Z1,…,Z7)组成,均配置内置ES-T型加速度计的ETNA型数字强震动仪,其中台站Z0位于山底土层上,台站Z1位于同一高度的山底基岩上,其它6个台站位于山脊不同高度的侏罗系基岩上(杨宇等,2011).图 1为自贡地形影响台阵的台站分布剖面示意图.
![]() 图 1 自贡地形影响台阵的台站位置剖面 示意图(引自王海云和谢礼立,2010)Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the stations location of Zigong topography array (after Wang and Xie,2010)
图 1 自贡地形影响台阵的台站位置剖面 示意图(引自王海云和谢礼立,2010)Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the stations location of Zigong topography array (after Wang and Xie,2010)汶川地震中自贡台阵的8个台站均获得了良好的三分量主震加速度记录.该台阵距离汶川地震震中约226.4 km,而距离最远的Z0与Z7两个台站的水平距离约为0.4 km(王海云,谢礼立,2010;凌代俭等,2013),因此可以认为地震波从震源传播到各个台站的传播路径是相同的,并且具有相同的震源效应,不同台站间地震动的差异受到局部场地效应的影响.台站Z0位于土层之上,其地震记录受到上覆土层和地形的共同影响,而台站Z1—Z7由于位于不同高度的基岩上,可以认为地形是影响其地震动记录差异的主要因素(杨宇等,2011).
本文使用台站Z1—Z7的三分量加速度记录,以台站Z1为参考台站,研究地形对地震动峰值加速度、 阿里亚斯烈度及90%地震动能量持时的影响,分析在地形效应影响下地震动峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度与斜坡稳定性的相关性.阿里亚斯烈度(Arias,1970)定义为一系列单位质量的单自由度体系(自振周期0—∞)所吸收的地震动能量总和,综合了地震动多持时及强度信息,具体表示为

式中:IAx为x方向的阿里亚斯烈度,单位为m/s;ax(t)为x方向的地震加速度时程,单位为m/s2;g为重力加速度;Td为地震加速度记录总的持续时间,单位为s. 90%地震动能量持时Ds(Dobry et al,1978)定义为阿里亚斯烈度达到5%—95%的时间间隔.各台站计算所得到的三分量地震动参数值如表 1所示.
表 1 各台站地震动峰值加速度、 阿里亚斯烈度IA及90%地震动能量持时Ds一览表Table 1. Measured PGA,Arias intensity (IA),Dobry duration (Ds) for the seven stations台站 IA/(m·s-1) PGA/(m·s-2) Ds/s EW NS UD EW NS UD EW NS UD Z1 0.046 0.055 0.022 0.225 0.265 0.147 90.46 89.89 91.46 Z2 0.068 0.069 0.028 0.274 0.304 0.157 120.85 115.22 121.50 Z3 0.090 0.090 0.034 0.333 0.323 0.176 121.09 116.59 122.36 Z4 0.081 0.093 0.030 0.274 0.323 0.157 122.46 117.75 128.78 Z5 0.111 0.142 0.036 0.333 0.421 0.157 120.88 117.15 122.03 Z6 0.150 0.163 0.039 0.412 0.421 0.196 120.62 117.72 123.71 Z7 0.119 0.125 0.029 0.304 0.451 0.147 120.30 117.01 121.16 2. 峰值加速度、 阿里亚斯烈度及持时随地形高度的变化
以台站Z1为地形参考台站,将地形放大系数K定义为

式中,Yj为台站Z2—Z7的三分量地震动参数值(地震动峰值加速度、 阿里亚斯烈度或地震动持时),Y1为台站Z1所对应分量的地震动参数值.
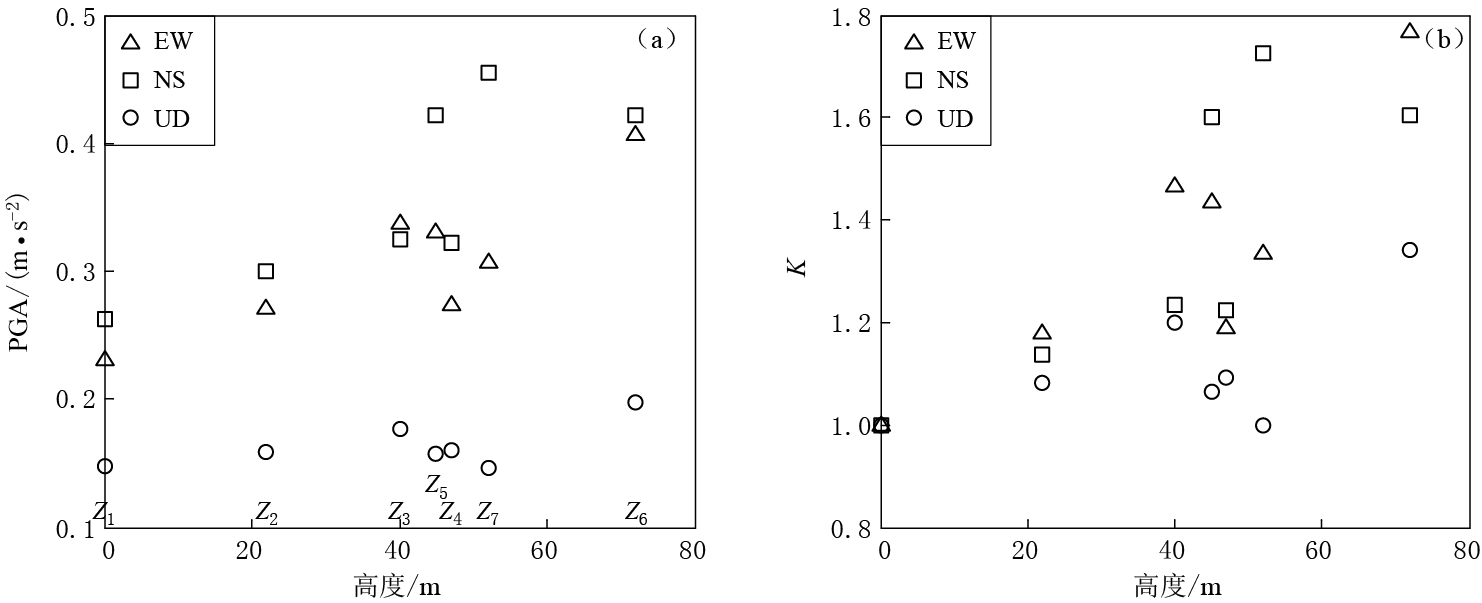
从图 2可以看出,各台站的峰值加速度及其放大系数整体上随台站高度的增加而增大,并且地形效应对峰值加速度水平向的影响大于竖直向.水平向峰值加速度EW分量由台站Z1(高度0 m)的0.225 m/s2增大到台站Z6(高度72 m)的0.412 m/s2,放大系数为1.18—1.77;NS分量由台站Z1的0.265 m/s2增大到台站Z7(高度52 m)的0.451 m/s2,放大系数为1.14—1.73. 竖直向峰值加速度由台站Z1的0.147 m/s2增大到台站Z6的0.196 m/s2,放大系数为1.08—1.34.
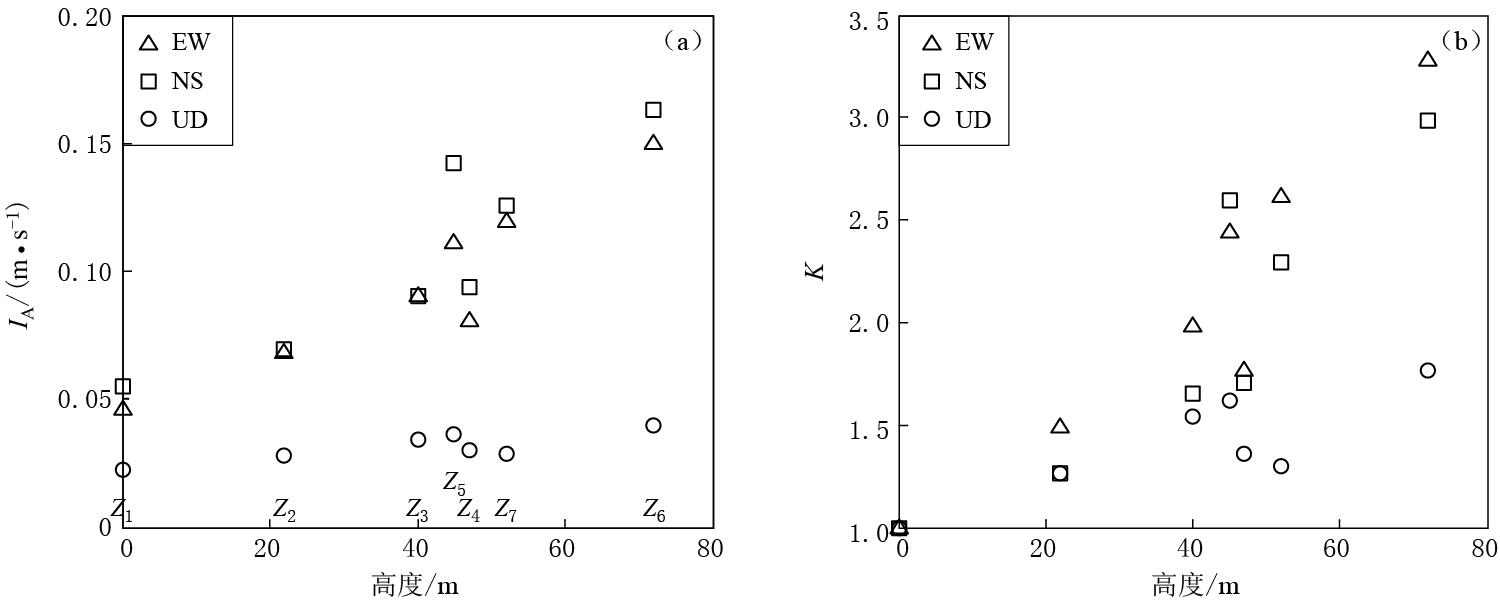
图 3给出了阿里亚斯烈度及其放大系数随台站高度的变化. 可以看出,地形场地对阿里亚斯烈度也有显著的放大效应,整体上阿里亚斯烈度及其放大系数随台站高度的增加而增大,地形效应对阿里亚斯烈度水平向的影响大于竖直向.水平向阿里亚斯烈度EW分量由台站Z1(高度0 m)的0.046 m/s增大到台站Z6(高度72 m)的0.150 m/s,放大系数为1.48—3.28;NS分量由台站Z1的0.055 m/s增大到台站Z6的0.163 m/s,放大系数为1.27—2.99. 竖直向阿里亚斯烈度由台站Z1的0.022 m/s增大到台站Z6的0.039 m/s,放大系数为1.26—1.77.
不同台站的峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度并非完全随台站高度的增加而增大. 例如:台站Z4的高度为47 m,大于台站Z5的高度(45 m),从表 1可以看出,台站Z4 NS分量和EW分量的峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度均小于台站Z5的相应数值;台站Z6(高度72 m)NS分量的峰值加速度也小于台站Z7(高度 52 m)的相应数值.这表明地形场地对地震动的影响机制较为复杂,高度并非影响地形放大效应的唯一因素.此外,地形效应对地震动影响是多方面的,影响到地震动幅值和频谱等特性(刘晶波,1996;王海云,谢礼立,2010),因此单一的地震动参数(如峰值加速度或阿里亚斯烈度)无法全面地刻画地形对地震动的影响.对比图 2与图 3可以看出,峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度随台站的变化具有不同的特征. 例如:台站Z7NS分量的峰值加速度放大系数为1.7,是所有台站NS分量峰值加速度放大系数的最大值;而其阿里亚斯烈度放大系数为2.3,并不是所有台站NS分量阿里亚斯烈度放大系数的最大值.因此,采用不同的地震动参数表征地形效应,其分析结果会有所差异. 在地震滑坡的研究中,考虑地形放大效应的地震滑坡稳定性分析需要选择合适的地震动参数,以合理地反映地形效应对斜坡稳定性的影响.
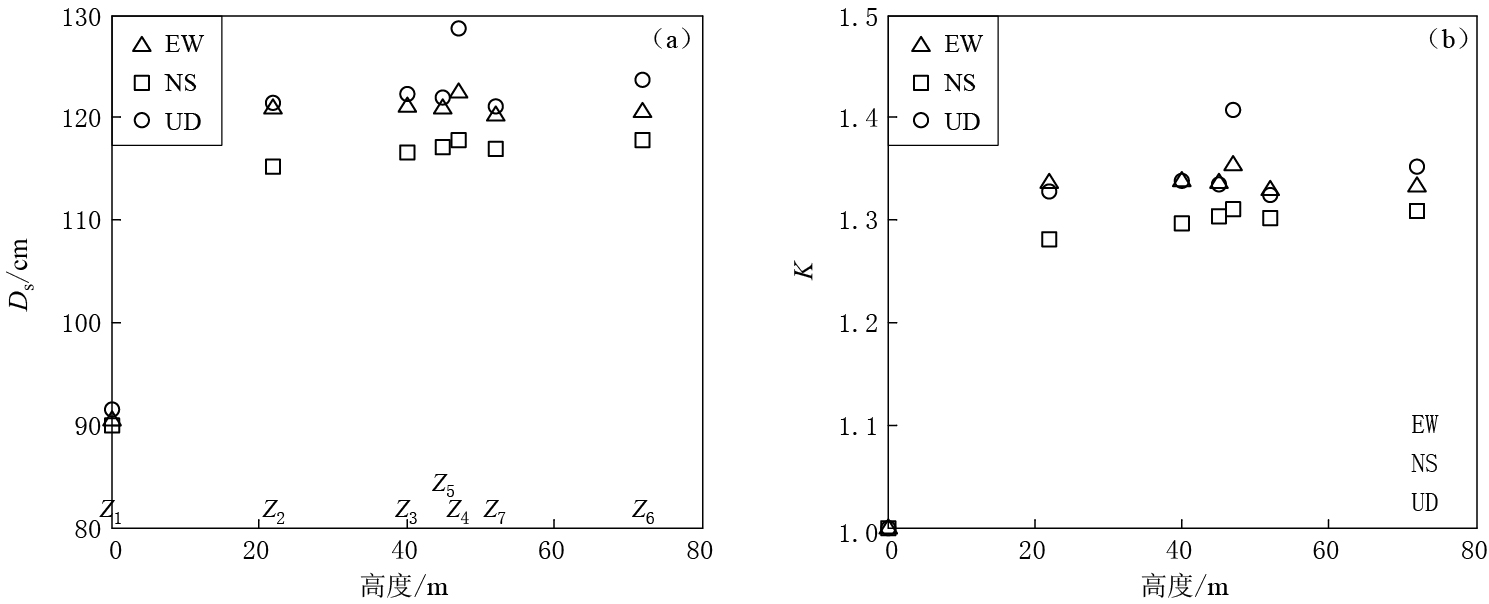
图 4给出了地震动持时及其放大系数随台站高度的变化. 可以看出,地形场地对地震动持时也有一定的影响. 山脊地形增大了地震动持时,不同地形高度的地震动记录持时并没有显著差异,不同分量的地震动持时也没有显著差异.参考台站Z1的三分量地震动持时约为90 s,EW分量持时为90.46 s,NS分量持时为89.89 s,UD分量持时为91.46 s; 台站Z2—Z7的三分量地震动持时均接近120 s,其放大系数约为1.33.
3. 地震动参数与斜坡稳定性的相关性
实际上,诸如台站Z1—Z7所记录到的地震动强度很难诱发斜坡失稳. 王秀英等(2012)的研究表明,汶川地震中整个龙门山震区诱发地震滑坡的地震动峰值加速度最小值平均约为0.98 m/s2,诱发地震滑坡的阿里亚斯烈度最小值约为0.2 m/s.但现实中可能存在一些斜坡,在某些因素(如斜坡已遭受一次强震破坏)影响下已处于临界滑动状态,随之而来的微弱震动(余震等)有可能触发其失稳.鉴于此,考虑到台站Z1—Z7台站水平分量地震动峰值加速度最小值约为0.20 m/s2,采用Newmark方法,本文假定存在一个临界加速度值为0.20 m/s2而处于临界滑动状态的斜坡,使各台站的地震动强度均能对斜坡稳定性产生影响,计算其在台站Z1—Z7水平分量地震动作用下所产生的Newmark累积位移(表 2),以对比考虑地形效应时峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度与斜坡稳定性的相关性.
表 2 各台站EW和NS分量的Newmark累积位移(DN)Table 2. Measured Newmark’s cumulative displacements DN of EW and NS components at the stations台站 EW分量DN/cm NS分量DN/cm Z1 0.01 0.05 Z2 0.03 0.16 Z3 0.13 0.30 Z4 0.07 0.32 Z5 0.33 0.88 Z6 0.71 1.07 Z7 0.26 0.59 由于台站布设密度不均匀等因素,实际工作中很难获取不同位置的地震动记录. 故考虑地形效应进行区域上的地震滑坡评估,通过地震动参数乘以放大系数进行分析较为适宜.对比地形效应对阿里亚斯烈度和峰值加速度的影响(图 2,3)可以看出,总体上二者随台站的高度变化趋势一致. 例如台站Z3的阿里亚斯烈度NS和EW分量均高于台站Z2,其峰值加速度NS和EW分量也同样高于台站Z2.但是阿里亚斯烈度与峰值加速度的变化趋势也不尽相同. 例如:台站Z6的阿里亚斯烈度NS分量为0.163 m/s,大于台站Z7(0.125 m/s),而台站Z6的峰值加速度NS分量为0.421 m/s2,小于台站Z7(0.451 m/s2).这是由于地形对地震动作用较为复杂,对地震动不同频段具有不同的影响所致(王海云,谢礼立,2010;杨宇等,2011;唐晖等,2012;凌代俭等,2013). 而峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度仅表征地震动的部分信息,地形效应反映在不同的地震动参数上则有所差异,这种差异会导致选用不同的地震动参数分析叠加地形效应影响的地震滑坡稳定性时,不能反映真实的地形影响.
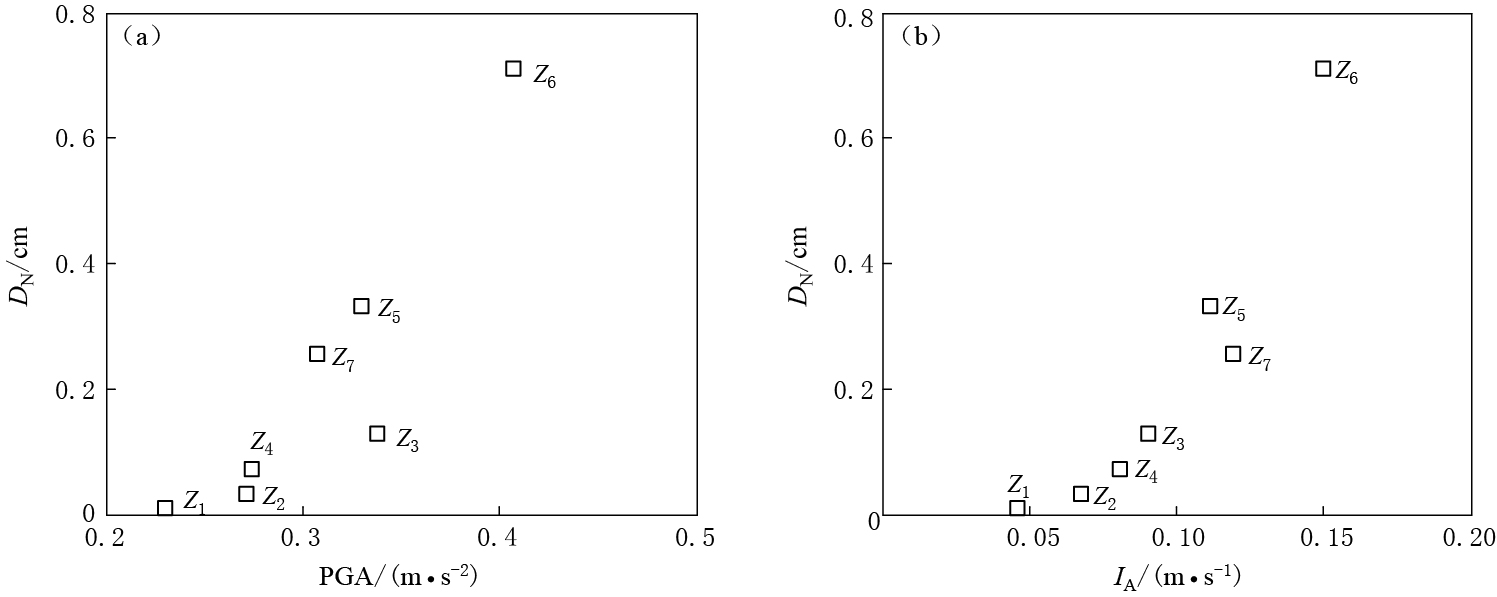
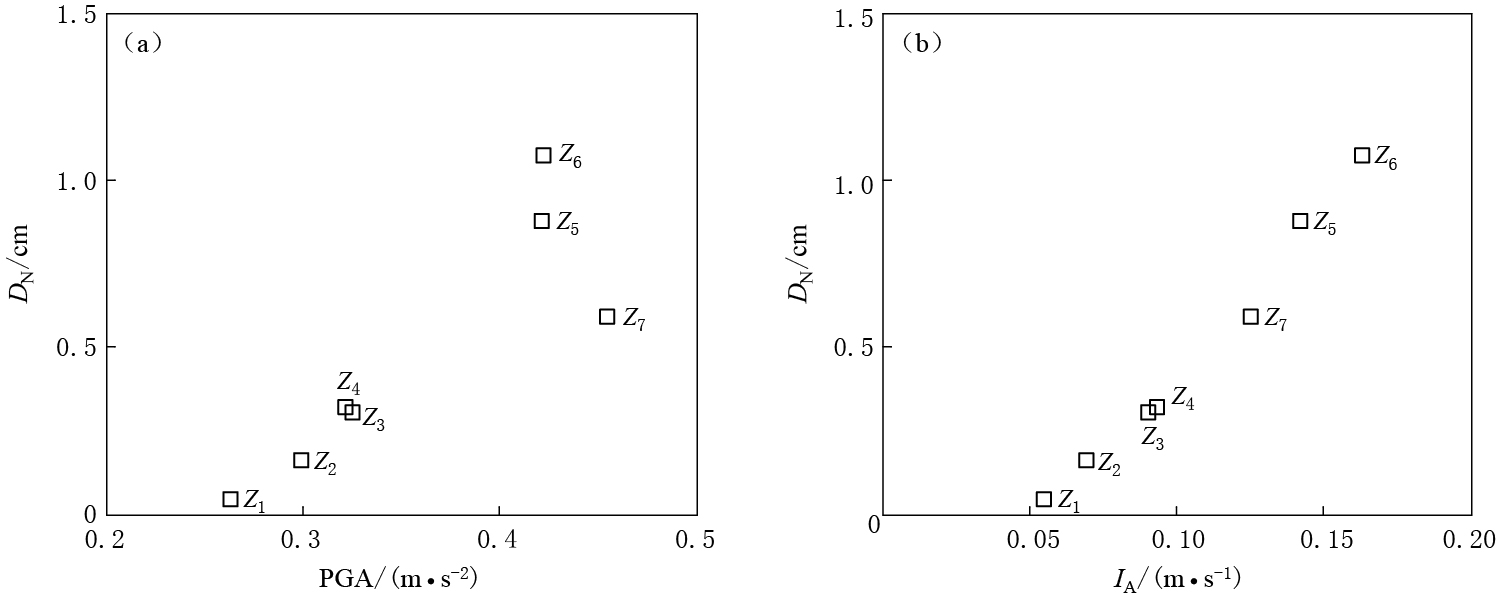
图 5给出了利用各台站EW分量加速度记录计算的Newmark累积位移随峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度的变化.可以看出:Newmark位移值按台站Z1,Z2,Z4,Z3,Z7,Z5,Z6的顺序依次增大,峰值加速度值按台站Z1,Z2,Z4,Z7,Z5,Z3,Z6的顺序增大,除台站Z3具有明显偏离外,Newmark位移值随峰值加速度的增大而增大;阿里亚斯烈度值按台站Z1,Z2,Z4,Z3,Z5,Z7,Z6的顺序增大,除台站Z5(相对台站Z7)稍有偏离外,Newmark位移值也随阿里亚斯烈度的增大而增大.
图 6给出了利用各台站NS分量加速度记录计算的Newmark累积位移随峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度的变化.可以看出:Newmark位移总体随着峰值加速度增大而增大,但二者的变化趋势在一些台站有所不同,台站Z6NS分量峰值加速度为0.421 m/s2,与台站Z5NS分量峰值加速度相同而小于台站Z7(0.451 m/s2),而斜坡在台站Z6地震动加速度NS分量作用下所产生的Newmark位移为1.07 cm,大于斜坡在台站Z5的0.88 cm和Z7台站的0.59 cm;阿里亚斯烈度值和Newmark位移值以相同的台站顺序同时增大,即Newmark位移完全随阿里亚斯烈度的增大而增大.
总体上看:Newmark位移随峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度的增大而增大,表明以峰值加速度或阿里亚斯烈度为地震动参数都可以很好地表征地形效应对斜坡稳定性的影响;相对于Newmark位移随峰值加速度曲折型的变化趋势,Newmark位移随阿里亚斯烈度增大而增大的趋势近乎呈直线型,表明阿里亚斯烈度可以更好地表征地形对地震动的影响,与在地震动作用下斜坡稳定性的相关性更强.
4. 讨论与结论
使用自贡地形影响台阵记录到的2008年汶川地震主震加速度记录,分析了地震动峰值加速度、 90%能量持时及阿里亚斯烈度随地形高度的变化,探讨了地形效应作用下峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度与地震作用下斜坡稳定性的相关性,得到以下结论:
1)地形对地震动的影响较为复杂,反映在不同地震动参数如峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度上具有不同的特征.地形场地对峰值加速度和阿里亚斯烈度均有显著的放大效应,整体上其放大效应随台站高度的增加而增大,水平向的放大效应大于竖直向,即水平向峰值加速度放大系数为1.1—1.8,阿里亚斯烈度放大系数为1.2—3.3;竖直向峰值加速度放大系数为1.1—1.3,阿里亚斯烈度放大系数为1.2—1.7.
2)地形场地对地震动持时也有一定的放大效应,不同高度及不同分量的放大效应没有显著差异,其放大系数均为1.3左右,这表明持时的地形放大效应或许不是地形加剧滑坡震害的重要影响因素.
3)地形对地震动强度、 持时具有放大效应,且影响较为复杂,因此考虑地震滑坡稳定性分析时需要选择合适的地震动参数来表征地形放大效应对斜坡破坏的影响.本文结果表明,阿里亚斯烈度和峰值加速度均能很好地表征地形对地震动的影响,与地震动对斜坡稳定性的影响具有很强的相关性;与峰值加速度相比,阿里亚斯烈度可以更好地表征地形对地震动的影响,与地震动作用下斜坡稳定性的相关性更强,是考虑地形效应影响的地震滑坡危险性的优选地震动参数.
国家强震动台网中心(CSMNC)为本文提供数据,中国地震局地球物理研究所王玉石副研究员提出建议,审稿专家对本文提出修改意见,作者在此一并表示感谢.
-
图 1 自贡地形影响台阵的台站位置剖面 示意图(引自王海云和谢礼立,2010)
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the stations location of Zigong topography array (after Wang and Xie,2010)
表 1 各台站地震动峰值加速度、 阿里亚斯烈度IA及90%地震动能量持时Ds一览表
Table 1 Measured PGA,Arias intensity (IA),Dobry duration (Ds) for the seven stations
台站 IA/(m·s-1) PGA/(m·s-2) Ds/s EW NS UD EW NS UD EW NS UD Z1 0.046 0.055 0.022 0.225 0.265 0.147 90.46 89.89 91.46 Z2 0.068 0.069 0.028 0.274 0.304 0.157 120.85 115.22 121.50 Z3 0.090 0.090 0.034 0.333 0.323 0.176 121.09 116.59 122.36 Z4 0.081 0.093 0.030 0.274 0.323 0.157 122.46 117.75 128.78 Z5 0.111 0.142 0.036 0.333 0.421 0.157 120.88 117.15 122.03 Z6 0.150 0.163 0.039 0.412 0.421 0.196 120.62 117.72 123.71 Z7 0.119 0.125 0.029 0.304 0.451 0.147 120.30 117.01 121.16 表 2 各台站EW和NS分量的Newmark累积位移(DN)
Table 2 Measured Newmark’s cumulative displacements DN of EW and NS components at the stations
台站 EW分量DN/cm NS分量DN/cm Z1 0.01 0.05 Z2 0.03 0.16 Z3 0.13 0.30 Z4 0.07 0.32 Z5 0.33 0.88 Z6 0.71 1.07 Z7 0.26 0.59 -
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 李孝波,王天虎,王怀强,柳耀阔,席书衡,赵扬. 北川沈家包斜坡场地地震效应研究. 振动与冲击. 2025(08): 241-250 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王者,刘云华. 贝叶斯反演:震源参数反演研究的重要方法与挑战. 地球物理学进展. 2024(05): 1771-1787 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈帅,苗则朗,吴立新. 基于修正岩土体强度参数的简化纽马克位移法地震滑坡危险性快速评估技术. 地震学报. 2022(03): 512-527 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 郝明辉,张郁山,赵凤新. 坡地地形对地震动特性的影响分析. 震灾防御技术. 2021(02): 229-236 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 唐世雄,邓广辉,刘衡秋. 斜坡抗震稳定性分析中拟静力法的应用研究. 城市地质. 2020(02): 181-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 卢育霞,王良,魏来,刘琨,车高凤,李少华. 利用场地表征参数研究岷漳地区地震动相对变化趋势. 防灾减灾工程学报. 2018(02): 359-366 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张海,史晨阳,尤红兵,苏振飞,季新星. 地形效应对于核电场地地震反应分析影响研究. 世界地震工程. 2018(03): 12-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 韩娜娜,单新建,宋小刚. 高空间分辨率数字高程模型测量技术及其在活断层研究中的应用. 地震学报. 2017(03): 436-450+452 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 卢育霞,刘琨,王良,魏来,李少华. 基于台阵记录的土层山体场地效应分析. 地震学报. 2017(06): 941-954 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(8)




 下载:
下载: